Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Apply the first law of thermodynamics to a resistor carrying a current i. Identify which of the quantities ∆Q, ∆U and ∆W are zero, positive and negative.
उत्तर
The battery is doing positive work on a resistor carrying current i. Thus, ∆W is positive. The work done on the resistor is used to increase its thermal energy; thus ∆Q is positive. As the temperature of the resistor rises, ∆U is positive.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
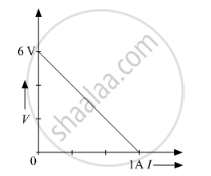
The plot of the variation of potential difference across a combination of three identical cells in series, versus current is shown below. What is the emf and internal resistance of each cell ?
A battery of emf 10 V and internal resistance 3 Ω is connected to a resistor. If the current in the circuit is 0.5 A, what is the resistance of the resistor? What is the terminal voltage of the battery when the circuit is closed?
Six lead-acid types of secondary cells each of emf 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.015 Ω are joined in series to provide a supply to a resistance of 8.5 Ω. What are the current drawn from the supply and its terminal voltage?
A resistor R is connected to a cell of-emf e and internal resistance r. The potential difference across the resistor R is found to be V. State the relation between e, V, Rand r.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected to two external resistance R1 and R2 and a perfect ammeter. The current in the circuit is measured in four different situations:
(i) without any external resistance in the circuit
(ii) with resistance R1 only
(iii) with R1 and R2 in series combination
(iv) with R1 and R2 in parallel combination
The currents measured in the four cases are 0.42 A, 1.05 A, 1.4 A and 4.2 A, but not necessarily in the order. Identify the currents corresponding to the four cases mentioned above.
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable resistor ‘R’. Plot a graph showing the variation of terminal potential ‘V’ with resistance R. Predict from the graph the condition under which ‘V’ becomes equal to ‘E’.
Two non-ideal batteries are connected in parallel. Consider the following statements:-
(A) The equivalent emf is smaller than either of the two emfs.
(B) The equivalent internal resistance is smaller than either of the two internal resistances.
Consider N = n1n2 identical cells, each of emf ε and internal resistance r. Suppose n1 cells are joined in series to form a line and n2 such lines are connected in parallel.
The combination drives a current in an external resistance R. (a) Find the current in the external resistance. (b) Assuming that n1 and n2 can be continuously varied, find the relation between n1, n2, R and r for which the current in R is maximum.
Do the electrodes in an electrolytic cell have fixed polarity like a battery?
A plate of area 10 cm2 is to be electroplated with copper (density 9000 kg m−3) to a thickness of 10 micrometres on both sides, using a cell of 12 V. Calculate the energy spent by the cell in the process of deposition. If this energy is used to heat 100 g of water, calculate the rise in the temperature of the water. ECE of copper = 3 × 10−7 kg C−1and specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1.
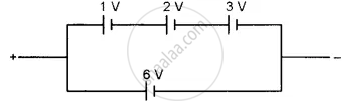
Find the emf of the battery shown in the figure:
A conductor of length 'l' is rotated about one of its ends at a constant angular speed 'ω' in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. Plot graphs to show variations of the emf induced across the ends of the conductor with (i) angular speed ω and (ii) length of the conductor l.
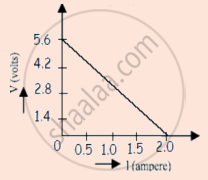
A straight line plot showing the terminal potential difference (V) of a cell as a function of current (I) drawn from it, is shown in the figure. The internal resistance of the cell would be then ______.
Five cells each of emf E and internal resistance r send the same amount of current through an external resistance R whether the cells are connected in parallel or in series. Then the ratio `("R"/"r")` is:
Three cells, each of emf E but internal resistances 2r, 3r and 6r are connected in parallel across a resistor R.
Obtain expressions for (i) current flowing in the circuit, and (ii) the terminal potential differences across the equivalent cell.
An ac generator generates an emf which is given by e = 311 sin (240 πt) V. Calculate:
- frequency of the emf.
- r.m.s. value of the emf.
Study the two circuits shown in the figure below. The cells in the two circuits are identical to each other. The resistance of the load resistor R is the same in both circuits.
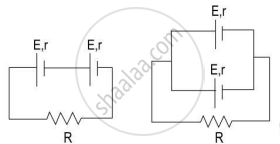
If the same current flows through the resistor R in both circuits, calculate the internal resistance of each cell in terms of the resistance of resistor R. Show your calculations.
