Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 100 pF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 24 V. It is connected to an uncharged capacitor of capacitance 20 pF. What will be the new potential difference across the 100 pF capacitor?
उत्तर
Given :
`C_1 = 100 "pF"`
V = 24 V
Charge on the capacitor `q = C_1V = 24 xx 100 "pC"`
Capacitance of the uncharged capacitor, `C_2 = 20 "pF"`
When the charged capacitor is connected with the uncharged capacitor, the net charge on the system of the capacitors becomes
`q_1 + q_2 = 24 xx 100 "qC"` ....(i)
The potential difference across the plates of the capacitors will be the same.
Thus,
`q_1/C_1 = q_2/C_2`
⇒ `q_1/100 = q_2/20`
⇒ `q_1 = 5q_2` ....................(ii)
From eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
`q_1+q_1/5 = 24 xx 100 "pc"`
⇒ `6q_1 = 5 xx 24 xx 100 "pC"`
⇒ `q_1 = (5xx24xx100)/(6) "pC"`
Now ,
`V_1 = q_1/C_1`
⇒ `(5xx24xx100 "pC")/(6xx100 "pF")` = 20 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between Conductors and Insulators.
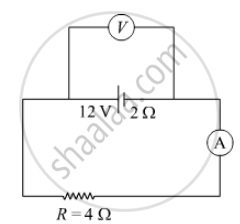
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
Explain the principle of a device that can build up high voltages of the order of a few million volts.
Is there any restriction on the upper limit of the high voltage set up in Van de Graff generator machine? Explain.
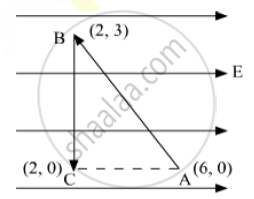
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
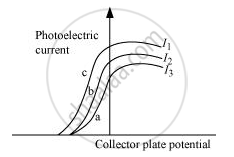
The figure shows a plot of three curves a, b, c, showing the variation of photocurrent vs collector plate potential for three different intensities I1, I2and I3 having frequencies v1, v2 and v3 respectively incident of a photosensitive surface.
Point out the two curves for which the incident radiations have same frequency but different intensities.
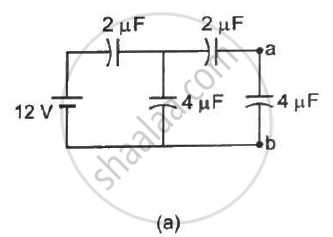
Find the potential difference `V_a - V_b` between the points a and b shown in each part of the figure.
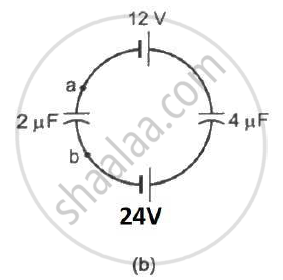
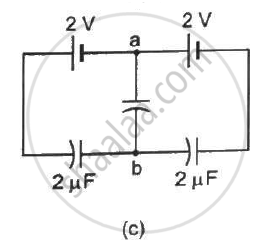
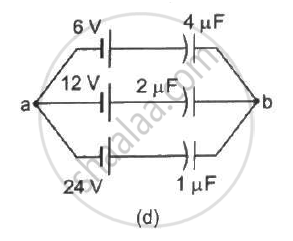
A charge of `+2.0 xx 10^-8 C` is placed on the positive plate and a charge of `-1.0 xx 10^-8 C` on the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance `1.2 xx 10^-3 "uF"` . Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
A charge of 1 µC is given to one plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 0⋅1 µF and a charge of 2 µC is given to the other plate. Find the potential difference developed between the plates.
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100 µF is charged to a potential difference of 50 V. (a) What is the magnitude of the charge on each plate? (b) The charging battery is disconnected and a dielectric of dielectric constant 2⋅5 is inserted. Calculate the new potential difference between the plates. (c) What charge would have produced this potential difference in absence of the dielectric slab. (d) Find the charge induced at a surface of the dielectric slab.
The unit of potential difference as used in electrical circuits is ________.
Two metal pieces having a potential difference of 800 V are 0.02 m apart horizontally. A particle of mass 1.96 × 10–15 kg is suspended in equilibrium between the plates. If e is the elementary charge, then charge on the particle is ______.
On moving a charge of Q coulomb by X cm, W J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is ______.
A and B are two points in an electric field. If the work done in carrying 4.0C of electric charge from A to B is 16.0 J, the potential difference between A and B is:
An α-particle and a proton are accelerate at same potential difference from rest. What will be the ratio of their final velocity?
If potential difference between the two ends of a metallic wire is doubled, drift speed of free electrons in the wire ______.
