Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2, find: the initial velocity of the ball.
उत्तर
Given, maximum height reached, s = 20 m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
Let 'u' be the initial velocity.
At the highest point, velocity = 0
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2gs
or, 0 - u2 = 2 (10) (20) m/s
or, u2 = -(400) m/s ...[Negative sign indicates that the motion is against gravity]
or, u = 20 m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the mass of one object is doubled?
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Let V and E be the gravitational potential and gravitational field at a distance r from the centre of a uniform spherical shell. Consider the following two statements :
(A) The plot of V against r is discontinuous.
(B) The plot of E against r is discontinuous.
A solid sphere of mass m and radius r is placed inside a hollow thin spherical shell of mass M and radius R as shown in the following figure . A particle of mass m' is placed on the line joining the two centres at a distance x from the point of contact of the sphere and the shell. Find the magnitude of the resultant gravitational force on this particle due to the sphere and the shell if (a) r < x < 2r, (b) 2r < x < 2R and (c) x > 2R.
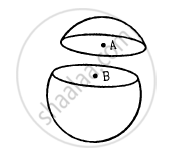
A thin spherical shell having uniform density is cut in two parts by a plane and kept separated as shown in the following figure. The point A is the centre of the plane section of the first part and B is the centre of the plane section of the second part. Show that the gravitational field at A due to the first part is equal in magnitude to the gravitational field at B due to the second part.
Gravity is another kind of ________. It exerts all through the ________. The Sun's gravity keeps the ___________ in their orbits. Gravity can only be felt with very large ________.
Explain the difference between g and G.
Answer the following question.
What are the dimensions of the universal gravitational constant?
If three equal masses m are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 1/m then what force acts on a particle of mass 2m placed at the centroid?
