Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A battery of 4 cell, each of e.m.f. 1.5 volt and internal resistance 0.5 Ω is connected to three resistances as shown in the figure. Calculate:
(i) The total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) The current through the cell.
(iii) The current through each resistance.
(iv) The p.d. across each resistance.
उत्तर
Let total e.m.f. of 4 cells = nE (n = number of cells)

E = 4 × 1.5
E = 6 volts ....(i)
Total internal resistance = nr (n = 4, r = 0.5 Ω)
Total internal resistance = 4 × 0.5 (in series)
= 2 Ω ....(ii)
Let total external resistance = X Ω
`1/"R" = 1/"R"_1 + 1/"R"_2` (R1 and R2 are in parallel)
`1/"R" = 1/4 + 1/12 = (3 + 1)/12 = 4/12`
R = `12/4 = 3 Ω`
Total external resistance = X = (R + R3)Ω (in series)
X = 3Ω + 7 Ω = 10Ω .....(iii)
Total resistance of the circuit = X + r = 10 + 2 = 12 Ω
Total current through the cell = `"E"/("X" + "r")` ...(as E = I (R + r))
I = `6/(10 + 2) = 0.5` A ....from (i), (ii) and (iii)
Current through resistor 4 Ω =
I1 = `("I" xx "R"_2)/("R"_1 + "R"_2)`
I1 = `(0.5 xx 12)/(4 + 12) = (0.5 xx 12)/16 = (0.5 xx 3)/4`
I1 = `1.5 xx 1/4 = 0.375`A
Similarly current through resistor 12 Ω = I2
I2 = `"I" xx "R"_1/("R"_1 + "R"_2)`
I2 = `0.5 xx 4/16 = 0.5 xx 1/4 = 1/8`
I2 = 0.125 A.
P.D. across resistance 7 Ω = V = I × R = 0.5 × 7 = 3.5 V
P.D. across resistance 4 Ω = V1 = V1 × R1 = 0.375 × 4 = 1.5 V
P.D. across resistance 12 Ω = V2 = I2 × R2 = 0.125 × 12 = 1.5 V.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the resistivity of semiconductor with the increase of temperature?
A cell of Emf 2 V and internal resistance 1.2 Ω is connected with an ammeter of resistance 0.8 Ω and two resistors of 4.5 Ω and 9 Ω as shown in the diagram below:
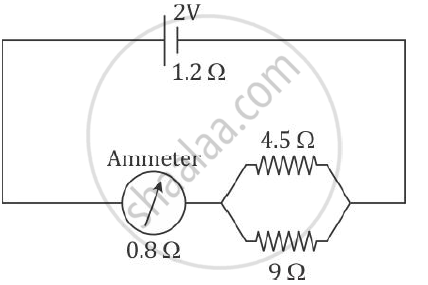
1) What would be the reading on the Ammeter?
2) What is the potential difference across the terminals of the cell?
A cell is used to send current to an external circuit.
- How does the voltage across its terminals compare with its e.m.f.?
- Under what condition is the e.m.f. of a cell equal to its terminal voltage?
A battery of e.m.f. 15 V and internal resistance 3 ohm is connected to two resistors of resistances 3 ohm and 6 ohm is series Find:
(a) the current through the battery
(b) the p.d. between the terminals of the battery.
What is the colour code for the insulation on the earth wire?
A cell of emf. 1.5 V and internal resistance 10 ohms is connected to a resistor of 5 ohms, with an ammeter in series see fig.. What is the reading of the ammeter?
Four cells, each of e.m.f. 1.5 V and internal resistance 2.0 ohms are connected in parallel. The battery of cells is connected to an external resistance of 2.5 ohms. Calculate:
(i) The total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) The current flowing in the external circuit.
(iii) The drop in potential across-the terminals of the cells.
When a resistance of 3Ω is connected across a cell, the current flowing is 0.5 A. On changing the resistance to 7Ω, the current becomes 0.25A. Calculate the e.m.f. and the internal resistance of the cell.
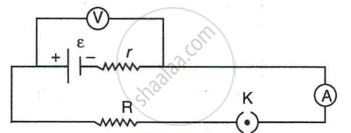
The diagram in Figure shows a cell of e.m.f. ε = 4 volt and internal resistance r = 2 ohm connected to an external resistance R = 8 ohm. The ammeter A measures the current in the circuit and the voltmeter V measures the terminal voltage across the cell. What will be the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter when
- the key K is open, and
- the key K is closed
A battery of e.m.f. 6·0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed. A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 3 A, the voltmeter reads 5.4 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
