Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A battery of 4 cell, each of e.m.f. 1.5 volt and internal resistance 0.5 Ω is connected to three resistances as shown in the figure. Calculate:
(i) The total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) The current through the cell.
(iii) The current through each resistance.
(iv) The p.d. across each resistance.
Solution
Let total e.m.f. of 4 cells = nE (n = number of cells)

E = 4 × 1.5
E = 6 volts ....(i)
Total internal resistance = nr (n = 4, r = 0.5 Ω)
Total internal resistance = 4 × 0.5 (in series)
= 2 Ω ....(ii)
Let total external resistance = X Ω
`1/"R" = 1/"R"_1 + 1/"R"_2` (R1 and R2 are in parallel)
`1/"R" = 1/4 + 1/12 = (3 + 1)/12 = 4/12`
R = `12/4 = 3 Ω`
Total external resistance = X = (R + R3)Ω (in series)
X = 3Ω + 7 Ω = 10Ω .....(iii)
Total resistance of the circuit = X + r = 10 + 2 = 12 Ω
Total current through the cell = `"E"/("X" + "r")` ...(as E = I (R + r))
I = `6/(10 + 2) = 0.5` A ....from (i), (ii) and (iii)
Current through resistor 4 Ω =
I1 = `("I" xx "R"_2)/("R"_1 + "R"_2)`
I1 = `(0.5 xx 12)/(4 + 12) = (0.5 xx 12)/16 = (0.5 xx 3)/4`
I1 = `1.5 xx 1/4 = 0.375`A
Similarly current through resistor 12 Ω = I2
I2 = `"I" xx "R"_1/("R"_1 + "R"_2)`
I2 = `0.5 xx 4/16 = 0.5 xx 1/4 = 1/8`
I2 = 0.125 A.
P.D. across resistance 7 Ω = V = I × R = 0.5 × 7 = 3.5 V
P.D. across resistance 4 Ω = V1 = V1 × R1 = 0.375 × 4 = 1.5 V
P.D. across resistance 12 Ω = V2 = I2 × R2 = 0.125 × 12 = 1.5 V.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name two factors on which the internal resistance of a cell depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
A battery of e.m.f 3.0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed.
A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 1.5 A, the voltmeter reads 2.7 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
A cell of e.m.f. 1.8V and internal resistance 2Ω is connected in series with an ammeter of resistance 0.7Ω and a resistor of 4.5Ω as shown in Fig.
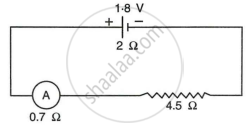
- What would be the reading of the ammeter?
- What is the potential difference across the terminals of the cell?
A battery of e.m.f. 15 V and internal resistance 3 ohm is connected to two resistors of resistances 3 ohm and 6 ohm is series Find:
(a) the current through the battery
(b) the p.d. between the terminals of the battery.
A cell of e.m.f. ε and internal resistance 𝔯 sends current 1.0 A when it is connected to an external resistance 1.9 Ω. But it sends current 0.5 A when it is connected to an external resistance 3.9 Ω. Calculate the values of ε and 𝔯.
What is the colour code for the insulation on the earth wire?
Four cells each of e.m.f. 2V and internal resistance 0.1 Ω are connected in series to an ammeter of negligible resistance, a 1.6 Ω resistor and an unknown resistor R1. The current in the circuit is 2A. Draw a labelled diagram and calculate:
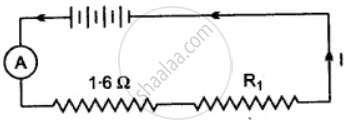
(i) Total resistance of the circuit,
(ii) Total e.m.f.
(iii) The value of R1 and
(iv) The p.d. across R1.
Study the diagram:
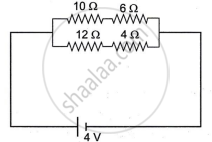
- Calculate the total resistance of the circuit.
- Calculate the current drawn from the cell.
- State whether the current through 10 Ω resistor is greater than, less than or equal to the current through the 12 Ω resistor.
Explain the meaning of the term internal resistance of a cell.
A battery of e.m.f. 6·0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed. A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 3 A, the voltmeter reads 5.4 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
