Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bicycle initially moving with a velocity 5.0 m s-1 accelerates for 5 s at a rate of 2 m s-2. What will be its final velocity?
उत्तर
Initial velocity of the bicycle, u = 5 m/s
Acceleration = 2 m/s2
Given time, t = 5 s
Let 'v' be the final velocity.
We know that, acceleration = Rate of change of velocity/time
= (Final velocity - Initial velocity)/time
Or 2 = (v - 5)/5
Or, 10 = (v - 5)
Or, v = 5 + 10
Or, v = 15 m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When will you say a body is at non-uniform acceleration?
A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h−1 to 60 km h−1 in 5 s. Find the acceleration of the bus.
Name the quantity which is measured by the area occupied under the velocity-time graph.
A boy is sitting on a merry-go-round which is moving with a constant speed of 10 m s−1. This means that the boy is :
When is the negative acceleration?
How can you find the following?
Velocity from acceleration – time graph.
Can you suggest a real-life example about the motion of a body from the following velocity – time graph?
A packet is dropped from a stationary helicopter, hovering at a height ‘h’ from ground level, reaches the ground in 12s. Calculate
- the value of h
- final velocity of packet on reaching the ground. (Take g = 9.8 ms−2)
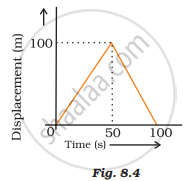
A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement–time graph is shown in Fig.8.4. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same.
The velocity-time graph (Fig. 8.5) shows the motion of a cyclist. Find (i) its acceleration (ii) its velocity and (iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds.

