Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bicycle initially moving with a velocity 5.0 m s-1 accelerates for 5 s at a rate of 2 m s-2. What will be its final velocity?
उत्तर
Initial velocity of the bicycle, u = 5 m/s
Acceleration = 2 m/s2
Given time, t = 5 s
Let 'v' be the final velocity.
We know that, acceleration = Rate of change of velocity/time
= (Final velocity - Initial velocity)/time
Or 2 = (v - 5)/5
Or, 10 = (v - 5)
Or, v = 5 + 10
Or, v = 15 m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Velocity is the rate of change of……………………… It is measured in.............. .
Define velocity. What is the SI unit of velocity ?
Find the initial velocity of a car which is stopped in 10 seconds by applying brakes. The retardation due to brakes is 2.5 m/s2.
Define velocity. State its unit.
If a stone and a pencil are dropped simultaneously in vacuum from the top of a tower, then which of the two will reach the ground first? Give reason.
Write three equations of uniformly accelerated motion relating the initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), time (t), acceleration (a) and displacement (S).
A body, initially at rest, starts moving with a constant acceleration 2 m s-2. Calculate: (i) the velocity acquired and (ii) the distance travelled in 5 s.
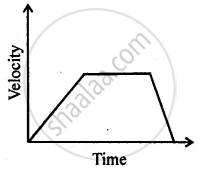
Can you suggest a real-life example about the motion of a body from the following velocity – time graph?
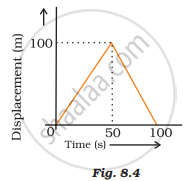
A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement–time graph is shown in Fig.8.4. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same.
An electron moving with a velocity of 5 × 104 ms−1 enters into a uniform electric field and acquires a uniform acceleration of 104 ms–2 in the direction of its initial motion.
(i) Calculate the time in which the electron would acquire a velocity double of its initial velocity.
(ii) How much distance the electron would cover at this time?
