Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A body, initially at rest, starts moving with a constant acceleration 2 m s-2. Calculate: (i) the velocity acquired and (ii) the distance travelled in 5 s.
उत्तर
Initial velocity u = 0 m/s
Acceleration a = 2 m/s2
Time t = 5 s
(i) Let 'v' be the final velocity.
Then, (v - u)/5 = 2
v = 10 m/s-1
(ii) Let 's' be the distance travelled.
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2as
We get,
(10) 2 - (0) 2 = 2(2) (s)
Thus, s = (100/4) m = 25 m
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A bus running at a speed of 18 km/h is stopped in 2.5 seconds by applying brakes. Calculate the retardation produced.
A body starting from rest travels with uniform acceleration. If it travels 100 m in 5 s, what is the value of acceleration ?
A train starting from stationary position and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed of 36 km per hour in 10 minutes. Find its acceleration.
When a car driver travelling at a speed of 10 m/s applies brakes and brings the car to rest in 20 s, then retardation will be :
A bicycle initially moving with a velocity 5.0 m s-1 accelerates for 5 s at a rate of 2 m s-2. What will be its final velocity?
Multiple choice Question. Select the correct option.
A body dropped from the top of a tower reaches the ground in 4s. Height of the tower is
How can you find the following?
Velocity from acceleration – time graph.
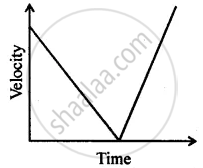
Can you suggest a real-life example about the motion of a body from the following velocity – time graph?
An electron moving with a velocity of 5 × 104 ms−1 enters into a uniform electric field and acquires a uniform acceleration of 104 ms–2 in the direction of its initial motion.
(i) Calculate the time in which the electron would acquire a velocity double of its initial velocity.
(ii) How much distance the electron would cover at this time?
When will you say a body is at uniform acceleration?
