Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A brick weighing 4.0 kg is dropped into a 1.0 m deep river from a height of 2.0 m. Assuming that 80% of the gravitational potential energy is finally converted into thermal energy, find this thermal energy is calorie.
उत्तर
Given:-
Mass of the brick, m = 4 kg
Total vertical distance travelled by the brick, h = 3 m
Percentage of gravitational potential energy converted to thermal energy = 80
Total change in potential energy of the brick = mgh = 4 × 10 × 3 = 120 J
`"Thermal Energy"=120xx80/100=96 J`
Thermal energy in calories is given by
`U=96/4.2=22.857"cal"approx23"cal"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A bullet of mass 20 g enters into a fixed wooden block with a speed of 40 m s−1 and stops in it. Find the change in internal energy during the process.
A block of mass 100 g slides on a rough horizontal surface. If the speed of the block decreases from 10 m s−1 to 5 m s−1, find the thermal energy developed in the process.
One end of a metal rod is kept in a furnace. In steady state, the temperature of the rod
A piece of charcoal and a piece of shining steel of the same surface area are kept for a long time in an open lawn in bright sun.
(a) The steel will absorb more heat than the charcoal
(b) The temperature of the steel will be higher than that of the charcoal
(c) If both are picked up by bare hand, the steel will be felt hotter than the charcoal
(d) If the two are picked up from the lawn and kept in a cold chamber, the charcoal will lose heat at a faster rate than the steel.
A pitcher with 1-mm thick porous walls contains 10 kg of water. Water comes to its outer surface and evaporates at the rate of 0.1 g s−1. The surface area of the pitcher (one side) = 200 cm2. The room temperature = 42°C, latent heat of vaporization = 2.27 × 106 J kg−1, and the thermal conductivity of the porous walls = 0.80 J s−1 m−1°C−1. Calculate the temperature of water in the pitcher when it attains a constant value.
Water at 50°C is filled in a closed cylindrical vessel of height 10 cm and cross sectional area 10 cm2. The walls of the vessel are adiabatic but the flat parts are made of 1-mm thick aluminium (K = 200 J s−1 m−1°C−1). Assume that the outside temperature is 20°C. The density of water is 100 kg m−3, and the specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J k−1g °C−1. Estimate the time taken for the temperature of fall by 1.0 °C. Make any simplifying assumptions you need but specify them.
The ends of a metre stick are maintained at 100°C and 0°C. One end of a rod is maintained at 25°C. Where should its other end be touched on the metre stick so that there is no heat current in the rod in steady state?
A metal rod of cross sectional area 1.0 cm2 is being heated at one end. At one time, the temperatures gradient is 5.0°C cm−1 at cross section A and is 2.5°C cm−1 at cross section B. Calculate the rate at which the temperature is increasing in the part AB of the rod. The heat capacity of the part AB = 0.40 J°C−1, thermal conductivity of the material of the rod = 200 W m−1°C−1. Neglect any loss of heat to the atmosphere
A composite slab is prepared by pasting two plates of thickness L1 and L2 and thermal conductivites K1 and K2. The slabs have equal cross-sectional area. Find the equivalent conductivity of the composite slab.
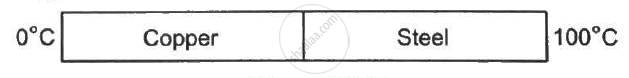
Figure (28-E2) shows a copper rod joined to a steel rod. The rods have equal length and equal cross sectional area. The free end of the copper rod is kept at 0°C and that of the steel rod is kept at 100°C. Find the temperature at the junction of the rods. Conductivity of copper = 390 W m−1°C−1 and that if steel = 46 W m−1°C−1.
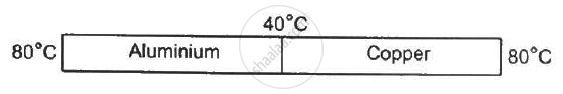
Following Figure shows an aluminium rod joined to a copper rod. Each of the rods has a length of 20 cm and area of cross section 0.20 cm2. The junction is maintained at a constant temperature 40°C and the two ends are maintained at 80°C. Calculate the amount of heat taken out from the cold junction in one minute after the steady state is reached. The conductivites are KAt = 200 W m−1°C−1 and KCu = 400 W m−1°C−1.
Suppose the bent part of the frame of the previous problem has a thermal conductivity of 780 J s−1 m−1 °C−1 whereas it is 390 J s−1 m−1°C−1 for the straight part. Calculate the ratio of the rate of heat flow through the bent part to the rate of heat flow through the straight part.
The two rods shown in following figure have identical geometrical dimensions. They are in contact with two heat baths at temperatures 100°C and 0°C. The temperature of the junction is 70°C. Find the temperature of the junction if the rods are interchanged.

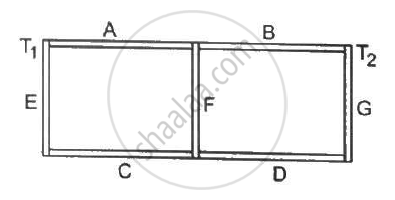
Seven rods A, B, C, D, E, F and G are joined as shown in the figure. All the rods have equal cross-sectional area A and length l. The thermal conductivities of the rods are KA = KC = K0, KB = KD = 2K0, KE = 3K0, KF = 4K0 and KG = 5K0. The rod E is kept at a constant temperature T1 and the rod G is kept at a constant temperature T2 (T2 > T1). (a) Show that the rod F has a uniform temperature T = (T1 + 2T2)/3. (b) Find the rate of heat flowing from the source which maintains the temperature T2.
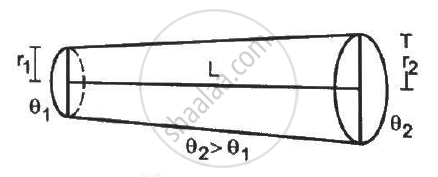
Find the rate of heat flow through a cross section of the rod shown in figure (28-E10) (θ2 > θ1). Thermal conductivity of the material of the rod is K.
A rod of negligible heat capacity has length 20 cm, area of cross section 1.0 cm2 and thermal conductivity 200 W m−1°C−1. The temperature of one end is maintained at 0°C and that of the other end is slowly and linearly varied from 0°C to 60°C in 10 minutes. Assuming no loss of heat through the sides, find the total heat transmitted through the rod in these 10 minutes.
Two bodies of masses m1 and m2 and specific heat capacities s1 and s2 are connected by a rod of length l, cross-sectional area A, thermal conductivity K and negligible heat capacity. The whole system is thermally insulated. At time t = 0, the temperature of the first body is T1 and the temperature of the second body is T2 (T2 > T1). Find the temperature difference between the two bodies at time t.
An amount n (in moles) of a monatomic gas at an initial temperature T0 is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a light piston. The surrounding air has a temperature Ts (> T0) and the atmospheric pressure is Pα. Heat may be conducted between the surrounding and the gas through the bottom of the cylinder. The bottom has a surface area A, thickness x and thermal conductivity K. Assuming all changes to be slow, find the distance moved by the piston in time t.
