Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Define vestigial organs.
- Write names of any two vestigial organs in the human body.
- Write name of those animals in which these vestigial organs are functional.
उत्तर
- Vestigial organs are degenerate organs that are inadequately developed and non-functional. They could be useful in certain related and unrelated species, as well as in ancestors.
- Vestigial organs in humans are:
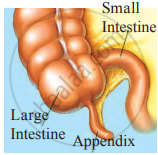
- Appendix
- Wisdom teeth
- Ear Muscles
- Tail-bone
-
- Appendix is fully functional in ruminants for digestion of cellulose.
- Ear pinna is useful in many animals like rabbits, cows, horses, etc.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of any two suitable examples explain the effect of anthropogenic actions on organic evolution.
Write the similarity between the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat. What do you infer from the above with reference to evolution?
Differentiate between analogy and homology giving one example each of plant and animal respectively.
Can the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat be considered homologous organs? Why or why not?
Enlist any four sequential evolutionary names of human ancestors.
Name any two temporary embryonic structures in vertebrates which provide evidence for evolution.
The organs which perform different functions but have the same basic structure are known as :
(a) homologous organs
(b) analogous organs
(c) homolytic organs
(d) analytic organs
The wings of a housefly and the wings of a sparrow are an example of :
(a) analogous organs
(b) vestigial organs
(c) respiratory organs
(d) homologous organs
You have potato, carrot, radish, sweet potato, tomato and ginger bought from the market in your jute bag. Identify two vegetables to represent the correct homologous structures.
(A) Potato and tomato
(B) Carrot and tomato
(C) Potato and sweet potato
(D) Carrot and radish
What do we call the degenerated or partially developed useless organs in living organisms? Enlist such organs in human body? How the same organs are useful in other animals?
Explain with suitable examples importance of anatomical evidence in evolution.
Answer the following question.
Wisdom teeth : Vestigial organs :: Lungfish : ....................
“Appearance of melanised moths post-industrialisation in England is a classic example of evolution by natural selection.” Explain.
Explain any three molecular (genetic) evidences in favour of organic evolution.
Answer the following question:
What are homologous structures? Give an example. Is it necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor? Justify your answer.
Long answer question.
Would you consider wings of butterfly and bat as homologous or analogous and why?
Similarities in the initial stages indicate the _______ evidence.
Find an odd one out.
I am a connecting link between reptiles and mammals. Who am I?
Write a short note:
Embryological evidences
Define the evidence of evolution shown in the figure.
Which evidence of evolution is shown in the given picture? Explain the importance of this evidence.

How do you differentiate homologous organs from analogous organs?
Homologous organs and vestigial organs are examples of ______ type of evidence in evolution.
Where is carbon dating used?
Homologous organs are:
Cucurbits do not develop thick and woody stem as they are:
Study of fossils is ______.
Evolutionary convergence is the development of:
Which is not a vestigial organ in a man?
Flippers of Penguins and Dolphins are examples of:
The study of fossil evidence of evolution is called ______
The evolutionary story of moths in England during industrialisation reveals, that 'evolution is apparently reversible'. Clarify this statement.
Complete the following diagram:

Complete the following conceptual picture:
Give examples of homologous organs and analogous organs in plants.
Give a definition of Palaeontology.
