Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A device Y is connected across an AC source of emf e = e0 sin ωt. The current through Y is given as i = i0 sin (ωt + π/2).
- Identify the device Y and write the expression for its reactance.
- Draw graphs showing a variation of emf and current with time over one cycle of AC for Y.
- How does the reactance of the device Y vary with the frequency of the AC? Show graphically.
- Draw the phasor diagram for device Y.
उत्तर
1. The device Y is a capacitor. Its reactance is `"X"_"C" = 1/(omega"C")`, where ω is the angular frequency of the applied emf and C is the capacitance of the capacitor.
2.

3. `"X"_"C" = 1/(omega"C") = 1/(2pi"fC")`. Thus `"X"_"C" prop 1/"f"`, where f is the frequency of AC.
Suppose C = `(1000/(2pi))`pF
For f = 100 Hz, XC = 1 × 107 Ω = 10 M Ω;
for f = 200 Hz, XC = 5 M Ω;
for f = 300 Hz, XC = `10/3` M Ω;
for f = 400 Hz, XC = 2.5 M Ω
for f = 500 Hz, XC = 2 M Ω and so on.
(1 M Ω = 106 Ω)
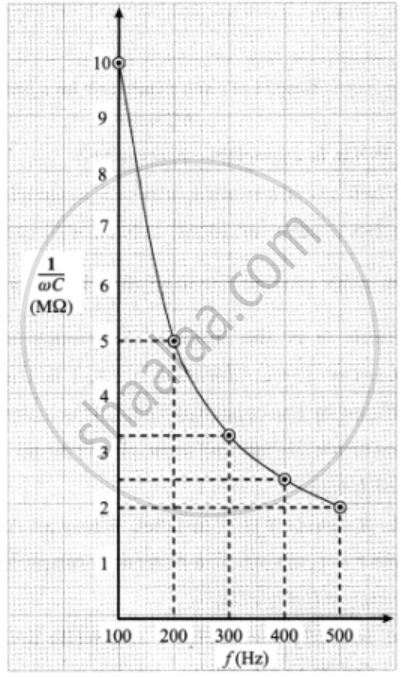
Variation of `1/(omega"C")` with f
4. Phasor diagram for a purely capacitive circuit
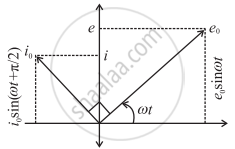
The phasor representing the peak emf (e0) makes an angle wt in an anticlockwise direction with respect to the horizontal axis. As the current leads the voltage by 90°, the phasor representing the peak current (i0) is turned 90° anticlockwise with respect to the phasor representing emf e0. The projections of these phasors on the vertical axis give instantaneous values of e and i.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by π/2 in an AC circuit containing an ideal capacitor ?
When an AC source is connected to a capacitor, there is a steady-state current in the circuit. Does it mean that the charges jump from one plate to the other to complete the circuit?
Is energy produced when a transformer steps up the voltage?
An AC source producing emf ε = ε0 [cos (100 π s−1)t + cos (500 π s−1)t] is connected in series with a capacitor and a resistor. The steady-state current in the circuit is found to be i = i1 cos [(100 π s−1)t + φ1) + i2 cos [(500π s−1)t + ϕ2]. So,
An AC source is rated 220 V, 50 Hz. The average voltage is calculated in a time interval of 0.01 s. It
A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V. Calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament.
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
A transformer has 50 turns in the primary and 100 in the secondary. If the primary is connected to a 220 V DC supply, what will be the voltage across the secondary?
Compare resistance and reactance.
Suppose the initial charge on the capacitor is 6 mC. What is the total energy stored in the circuit initially? What is the total energy at later time?
A.C. power is transmitted from a power house at a high voltage as ______.
When an ac voltage of 220 V is applied to the capacitor C, then ______.
A capacitor has capacitance C and reactance X, if capacitance and frequency become double, then reactance will be ______.
An alternating current of 1.5 mA and angular frequency 300 rad/sec flows through a 10 k Ω resistor and a 0.50 µF capacitor in series. Find the rms voltage across the capacitor and impedance of the circuit.
Explain why the reactance provided by a capacitor to an alternating current decreases with increasing frequency.
An iron cored coil is connected in series with an electric bulb with an AC source as shown in figure. When iron piece is taken out of the coil, the brightness of the bulb will ______.
An a.c. source generating a voltage ε = ε0 sin ωt is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the expression for the current I flowing through it. Plot a graph of ε and I versus ωt to show that the current is ahead of the voltage by π/2.
A resistor of 50 Ω, a capacitor of `(25/pi)` µF and an inductor of `(4/pi)` H are connected in series across an ac source whose voltage (in volts) is given by V = 70 sin (100 πt). Calculate:
- the net reactance of the circuit
- the impedance of the circuit
- the effective value of current in the circuit.
