Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V. Calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament.
उत्तर
Power of the bulb, P = 60 W
Voltage at the bulb, V = 220 V
RMS value of alternating voltage, Erms = 220 V
P = V2R,
where R = resistance of the bulb
`therefore R = v^2/P = (220xx220)/60`
=806.67
Peak value of voltage (E_0) is given by,
`i_0 = E_0/R`
`⇒ i_0 = (311.08)/806.67 = 0.39 A `
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by π/2 in an AC circuit containing an ideal capacitor ?
Is energy produced when a transformer steps up the voltage?
A capacitor acts as an infinite resistance for ______.
An AC source producing emf ε = ε0 [cos (100 π s−1)t + cos (500 π s−1)t] is connected in series with a capacitor and a resistor. The steady-state current in the circuit is found to be i = i1 cos [(100 π s−1)t + φ1) + i2 cos [(500π s−1)t + ϕ2]. So,
An AC source is rated 220 V, 50 Hz. The average voltage is calculated in a time interval of 0.01 s. It
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
A transformer has 50 turns in the primary and 100 in the secondary. If the primary is connected to a 220 V DC supply, what will be the voltage across the secondary?
A device Y is connected across an AC source of emf e = e0 sin ωt. The current through Y is given as i = i0 sin (ωt + π/2).
- Identify the device Y and write the expression for its reactance.
- Draw graphs showing a variation of emf and current with time over one cycle of AC for Y.
- How does the reactance of the device Y vary with the frequency of the AC? Show graphically.
- Draw the phasor diagram for device Y.
A capacitor has capacitance C and reactance X, if capacitance and frequency become double, then reactance will be ______.
When an AC voltage of 220 V is applied to the capacitor C ______.
- the maximum voltage between plates is 220 V.
- the current is in phase with the applied voltage.
- the charge on the plates is in phase with the applied voltage.
- power delivered to the capacitor is zero.
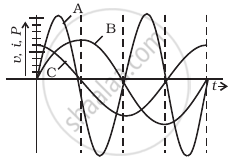
A device ‘X’ is connected to an a.c source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in figure.
- Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
- What is the average power consumption over a cycle?
- Identify the device ‘X’.
Explain why the reactance provided by a capacitor to an alternating current decreases with increasing frequency.
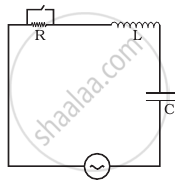
In the LCR circuit shown in figure, the ac driving voltage is v = vm sin ωt.
- Write down the equation of motion for q (t).
- At t = t0, the voltage source stops and R is short circuited. Now write down how much energy is stored in each of L and C.
- Describe subsequent motion of charges.
An a.c. source generating a voltage ε = ε0 sin ωt is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the expression for the current I flowing through it. Plot a graph of ε and I versus ωt to show that the current is ahead of the voltage by π/2.
A resistor of 50 Ω, a capacitor of `(25/pi)` µF and an inductor of `(4/pi)` H are connected in series across an ac source whose voltage (in volts) is given by V = 70 sin (100 πt). Calculate:
- the net reactance of the circuit
- the impedance of the circuit
- the effective value of current in the circuit.
