Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The household supply of electricity is at 220 V (rms value) and 50 Hz. Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the rms value to zero.
उत्तर
RMS value of voltage, Erms = 220 V,
Frequency of alternating current, f = 50 Hz
(a) Peak value of voltage `(E_0)` is given by,
`E_0 = E_{rms] sqrt2`
where Erms = root mean square value of voltage
`E_0 = E_{rms} sqrt2`
`⇒ E_0 =sqrt2xx220`
`⇒ E_0 = 311.08 V = 311 V`
(b) Voltage (E) is given by,
`E = E_0 sin omegat,`
where E0 = peak value of voltage
Time taken for the current to reach zero from the rms value = Time taken for the current to reach the rms value from zero
In one complete cycle, current starts from zero and again reaches zero.
So, first we need to find the time taken for the current to reach the rms value from zero.
`As E = E_0/sqrt2`
`⇒ E_0/sqrt2 = E_0 sin omega t`
`⇒ t = pi/(4 omega) = pi/(4xx2pif)`
`⇒ t = pi/(8pi50) = 1/400`
⇒ t = 2.5 ms
Thus, the least possible time in which voltage can change from the rms value to zero is 2.5 ms.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A device X is connected across an ac source of voltage V = V0 sin ωt. The current through X is given as
`I = I_0 sin (omega t + pi/2 )`
1) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
2) Draw graphs showing the variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of ac, for X.
3) How does the reactance of the device X vary with the frequency of the ac? Show this variation graphically.
4) Draw the phasor diagram for the device X.
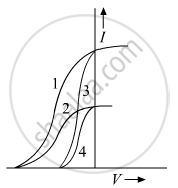
The given graph shows the variation of photo-electric current (I) versus applied voltage (V) for two difference photosensitive materials and for two different intensities of the incident radiations. Identify the pairs of curves that correspond to different materials but same intensity of incident radiation.
In a series LCR circuit connected to an ac source of variable frequency and voltage ν = vm sin ωt, draw a plot showing the variation of current (I) with angular frequency (ω) for two different values of resistance R1 and R2 (R1 > R2). Write the condition under which the phenomenon of resonance occurs. For which value of the resistance out of the two curves, a sharper resonance is produced? Define Q-factor of the circuit and give its significance.
Two alternating currents are given by `i_1 = i_0 sin wt and i_2 = i_0 sin (wt + pi/3)` Will the rms values of the currents be equal or different?
Can a hot-wire ammeter be used to measure a direct current of constant value? Do we have to change the graduations?
An alternating current is given by i = i1 cos ωt + i2 sin ωt. The rms current is given by
A constant current of 2.8 A exists in a resistor. The rms current is
The peak power consumed by a resistive coil, when connected to an AC source, is 80 W. Find the energy consumed by the coil in 100 seconds, which is many times larger than the time period of the source.
A capacitor of capacitance 10 μF is connected to an oscillator with output voltage ε = (10 V) sin ωt. Find the peak currents in the circuit for ω = 10 s−1, 100 s−1, 500 s−1 and 1000 s−1.
A resistor of resistance 100 Ω is connected to an AC source ε = (12 V) sin (250 π s−1)t. Find the energy dissipated as heat during t = 0 to t = 1.0 ms.
The peak voltage of an ac supply is 300 V. What is the rms voltage?
The rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current?
A circuit containing a 80 mH inductor and a 60 µF capacitor in series is connected to a 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(a) Obtain the current amplitude and rms values.
(b) Obtain the rms values of potential drops across each element.
(c) What is the average power transferred to the inductor?
(d) What is the average power transferred to the capacitor?
(e) What is the total average power absorbed by the circuit?
[‘Average’ implies ‘averaged over one cycle’.]
A small town with a demand of 800 kW of electric power at 220 V is situated 15 km away from an electric plant generating power at 440 V. The resistance of the two wire line carrying power is 0.5 Ω per km. The town gets power from the line through a 4000-220 V step-down transformer at a sub-station in the town.
(a) Estimate the line power loss in the form of heat.
(b) How much power must the plant supply, assuming there is negligible power loss due to leakage?
(c) Characterise the step up transformer at the plant.
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is T = `2π sqrt"L"/"g"`. The measured value of L is 20.0 cm known to have 1 mm accuracy and the time for 100 oscillations of the pendulum is found to be 90 s using a wristwatch of ls resolution. The accuracy in the determination of g is:
Phase diffn between voltage and current in a capacitor in A.C Circuit is.
In a transformer Np = 500, Ns = 5000. Input voltage is 20 volt and frequency is 50 HZ. Then in the output, we have,
