Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A circuit containing a 80 mH inductor and a 60 µF capacitor in series is connected to a 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(a) Obtain the current amplitude and rms values.
(b) Obtain the rms values of potential drops across each element.
(c) What is the average power transferred to the inductor?
(d) What is the average power transferred to the capacitor?
(e) What is the total average power absorbed by the circuit?
[‘Average’ implies ‘averaged over one cycle’.]
उत्तर
Inductance, L = 80 mH = 80 × 10−3 H
Capacitance, C = 60 μF = 60 × 10−6 F
Supply voltage, V = 230 V
Frequency, v = 50 Hz
Angular frequency, ω = 2πv = 100 π rad/s
Peak voltage, V0 = `"V" sqrt2 = 230 sqrt2 "V"`
(a) Maximum current is given as:
I0 = `"V"_0/((ω"L" - 1/(ω"C")))`
= `(230 sqrt3)/((100π xx 80 xx 10^-3 - 1/(100π xx 60 xx 10^-6)))`
= `(230 sqrt2)/((8π - 1000/(6π)))`
= −11.63 A
The negative sign appears because `ω"L" < 1/(ω"C")`.
Amplitude of maximum current, |I0| = 11.63 A
Hence, rms value of current, I = `"I"_0/sqrt2 = (-11.63)/sqrt2` = −8.22 A
(b) Potential difference across the inductor,
VL = I × ωL
= 8.22 × 100 π × 80 × 10−3
= 206.61 V
Potential difference across the capacitor,
Ve = `"I" xx 1/(ω"C")`
= `8.22 xx 1/(100π xx 60 xx 10^-6)`
= 436.3 V
(c) Average power consumed by the inductor is zero as actual voltage leads the current by `π/2`.
(d) Average power consumed by the capacitor is zero as voltage lags current by `π/2`.
(e) The total power absorbed (averaged over one cycle) is zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two alternating currents are given by `i_1 = i_0 sin wt and i_2 = i_0 sin (wt + pi/3)` Will the rms values of the currents be equal or different?
An alternating current of peak value 14 A is used to heat a metal wire. To produce the same heating effect, a constant current i can be used, where i is
The household supply of electricity is at 220 V (rms value) and 50 Hz. Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the rms value to zero.
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
In a series RC circuit with an AC source, R = 300 Ω, C = 25 μF, ε0 = 50 V and ν = 50/π Hz. Find the peak current and the average power dissipated in the circuit.
Answer the following question.
A small town with a demand of 1200 kW of electric power at 220 V is situated 20 km away from an electric plant generating power at 440 V. The resistance of the two wirelines carrying power is 0.5 Ω per km. The town gets the power from the line through a 4000-220 V step-down transformer at a sub-station in the town. Estimate the line power loss in the form of heat.
The rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current?
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is T = `2π sqrt"L"/"g"`. The measured value of L is 20.0 cm known to have 1 mm accuracy and the time for 100 oscillations of the pendulum is found to be 90 s using a wristwatch of ls resolution. The accuracy in the determination of g is:
The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12-watt light bulb. The value of the peak current is ______.
In the Figure below, the current-voltage graphs for a conductor are given at two different temperatures, T1 and T2.
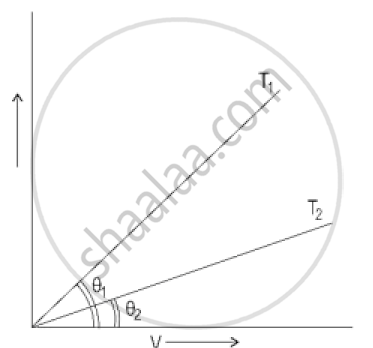
- At which temperature T1 or T2 is the resistance higher?
- Which temperature (T1 or T2) is higher?
