Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A circuit containing a 80 mH inductor and a 60 µF capacitor in series is connected to a 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(a) Obtain the current amplitude and rms values.
(b) Obtain the rms values of potential drops across each element.
(c) What is the average power transferred to the inductor?
(d) What is the average power transferred to the capacitor?
(e) What is the total average power absorbed by the circuit?
[‘Average’ implies ‘averaged over one cycle’.]
Solution
Inductance, L = 80 mH = 80 × 10−3 H
Capacitance, C = 60 μF = 60 × 10−6 F
Supply voltage, V = 230 V
Frequency, v = 50 Hz
Angular frequency, ω = 2πv = 100 π rad/s
Peak voltage, V0 = `"V" sqrt2 = 230 sqrt2 "V"`
(a) Maximum current is given as:
I0 = `"V"_0/((ω"L" - 1/(ω"C")))`
= `(230 sqrt3)/((100π xx 80 xx 10^-3 - 1/(100π xx 60 xx 10^-6)))`
= `(230 sqrt2)/((8π - 1000/(6π)))`
= −11.63 A
The negative sign appears because `ω"L" < 1/(ω"C")`.
Amplitude of maximum current, |I0| = 11.63 A
Hence, rms value of current, I = `"I"_0/sqrt2 = (-11.63)/sqrt2` = −8.22 A
(b) Potential difference across the inductor,
VL = I × ωL
= 8.22 × 100 π × 80 × 10−3
= 206.61 V
Potential difference across the capacitor,
Ve = `"I" xx 1/(ω"C")`
= `8.22 xx 1/(100π xx 60 xx 10^-6)`
= 436.3 V
(c) Average power consumed by the inductor is zero as actual voltage leads the current by `π/2`.
(d) Average power consumed by the capacitor is zero as voltage lags current by `π/2`.
(e) The total power absorbed (averaged over one cycle) is zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two alternating currents are given by `i_1 = i_0 sin wt and i_2 = i_0 sin (wt + pi/3)` Will the rms values of the currents be equal or different?
Can a hot-wire ammeter be used to measure a direct current of constant value? Do we have to change the graduations?
An electric bulb is designed to operate at 12 volts DC. If this bulb is connected to an AC source and gives normal brightness, what would be the peak voltage of the source?
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
A capacitor of capacitance 10 μF is connected to an oscillator with output voltage ε = (10 V) sin ωt. Find the peak currents in the circuit for ω = 10 s−1, 100 s−1, 500 s−1 and 1000 s−1.
In a series RC circuit with an AC source, R = 300 Ω, C = 25 μF, ε0 = 50 V and ν = 50/π Hz. Find the peak current and the average power dissipated in the circuit.
The peak voltage of an ac supply is 300 V. What is the rms voltage?
When a voltage measuring device is connected to AC mains, the meter shows the steady input voltage of 220V. This means ______.
In the Figure below, the current-voltage graphs for a conductor are given at two different temperatures, T1 and T2.
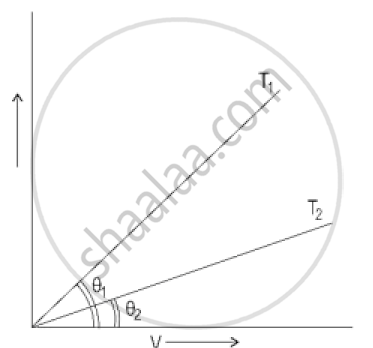
- At which temperature T1 or T2 is the resistance higher?
- Which temperature (T1 or T2) is higher?
