Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metal rod of square cross-sectional area A having length l has current I flowing through it when a potential difference of V volt is applied across its ends (figure I). Now the rod is cut parallel to its length into two identical pieces and joined as shown in figure II. What potential difference must be maintained across the length of 2l. so that the current in the rod is still I?

उत्तर
From Ohm's law, we have
\[V = IR\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = I\rho\frac{l}{A} . . . . . (1)\]
When the rod is cut parallel, and rejoined by length, the length of the conductor becomes 2l, whereas the area decrease to
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
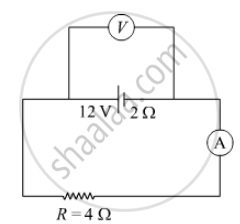
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
A charge of `+2.0 xx 10^-8 C` is placed on the positive plate and a charge of `-1.0 xx 10^-8 C` on the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance `1.2 xx 10^-3 "uF"` . Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
A charge of 20 µC is placed on the positive plate of an isolated parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 10 µF. Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
The capacitance between the adjacent plates shown in figure is 50 nF. A charge of 1⋅0 µC is placed on the middle plate. (a) What will be the charge on the outer surface of the upper plate? (b) Find the potential difference developed between the upper and the middle plates.

Answer the following question:
Find the expression for the resistivity of a material.
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
If a positive charge moves in the direction of the electric field ______.
A and B are two points in an electric field. If the work done in carrying 4.0C of electric charge from A to B is 16.0 J, the potential difference between A and B is:
Can there be a potential difference between two adjacent conductors carrying the same charge?
If potential difference between the two ends of a metallic wire is doubled, drift speed of free electrons in the wire ______.
