Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
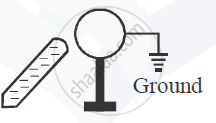
A metal sphere is kept on an insulting stands. A negatively charged rod is brought near it, then the sphere is earthed as shown. On removing the earthing, and taking the negatively charged rod away, what will be the nature of charge on the sphere? Give reason for your answer.
उत्तर १
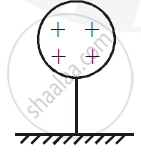
There will be positive charge on the sphere.
Reason :
Negatively charged rod will induce positive charge on the sphere and negative charge well move in ground from other end.
उत्तर २
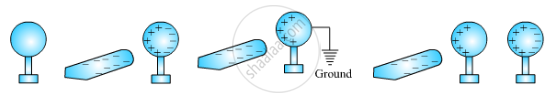
When we bring a negatively charged rod near the metal sphere, the free electrons in the sphere move away due to repulsion force and start piling up at the other end. The rear end becomes positively charged due to the deficit of electrons. After connecting the sphere to the ground, the electrons flow to the ground while the positive charges at the rear end remain as it is due to the attractive force of the negative charges on the rod. When the sphere is disconnected from the ground and the charged rod is removed, the positive charge spreads uniformly over the sphere as shown in the Figure below:
संबंधित प्रश्न
A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why?
How should the two resistances of 2 ohms each be connected so as to produce an equivalent resistance of 1 ohm?
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of potential difference 3 V.
How would you connect two resistors in series? Draw a diagram. Calculate the total equivalent resistance.
How does an increase in the temperature affect the specific resistance of a :
(i) Metal and
(ii) Semiconductor ?
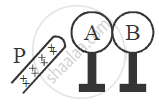
Two metallic spheres A and B kept on insulating stands are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod P is brought near the sphere A as shown in the figure. The two spheres are separated from each other, and the rod P is removed. What will be the nature of charges on spheres A and B?
What is non ohmic device?
Write a short note on superconductors?
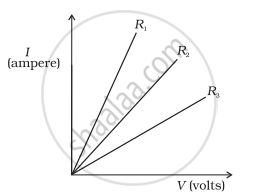
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Which of the following is true?
Consider a current carrying wire (current I) in the shape of a circle. Note that as the current progresses along the wire, the direction of j (current density) changes in an exact manner, while the current I remain unaffected. The agent that is essentially responsible for is ______.
