Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metallic metre stick moves with a velocity of 2 m s−1 in a direction perpendicular to its length and perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.2 T. Find the emf induced between the ends of the stick.
उत्तर
Given:-
Length of the stick, l = 1 m
Magnetic field, B = 0.2 T
Velocity of the stick, v = 2 m/s
Thus, we get
Induced emf, e = Blv = 0.2 × 1 × 2 = 0.4 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A square loop of side 12 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is moved with a velocity of 8 cm s−1 in the positive x-direction in an environment containing a magnetic field in the positive z-direction. The field is neither uniform in space nor constant in time. It has a gradient of 10−3 T cm−1 along the negative x-direction (that is it increases by 10− 3 T cm−1 as one move in the negative x-direction), and it is decreasing in time at the rate of 10−3 T s−1. Determine the direction and magnitude of the induced current in the loop if its resistance is 4.50 mΩ.
(a) Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance between a long straight wire and a square loop of side an as shown in the figure.
(b) Now assume that the straight wire carries a current of 50 A and the loop is moved to the right with a constant velocity, v = 10 m/s.
Calculate the induced emf in the loop at the instant when x = 0.2 m.
Take a = 0.1 m and assume that the loop has a large resistance.

An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
A metallic rod of ‘L’ length is rotated with angular frequency of ‘ω’ with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius L, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is presents everywhere. Deduce the expression for the emf between the centre and the metallic ring.
Consider the following statements:-
(A) An emf can be induced by moving a conductor in a magnetic field.
(B) An emf can be induced by changing the magnetic field.
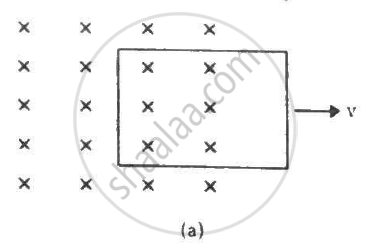
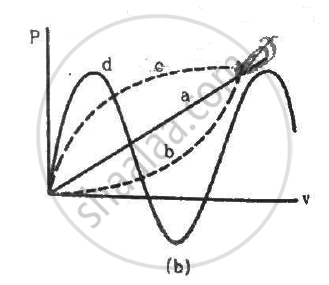
Figure shows a conducting loop being pulled out of a magnetic field with a speed v. Which of the four plots shown in figure (b) may represent the power delivered by the pulling agent as a function of the speed v?
The flux of magnetic field through a closed conducting loop changes with time according to the equation, Φ = at2 + bt + c. (a) Write the SI units of a, b and c. (b) If the magnitudes of a, b and c are 0.20, 0.40 and 0.60 respectively, find the induced emf at t = 2 s.
A conducting circular loop having a radius of 5.0 cm, is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.50 T. It is removed from the field in 0.50 s. Find the average emf produced in the loop during this time.
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10 cm as shown in figure. A uniform wire of length 80 cm and resistance 4.0 Ω is bent into a square frame and is placed with one side along a diameter of the cylindrical region. If the magnetic field increases at a constant rate of 0.010 T/s, find the current induced in the frame.
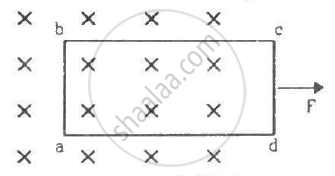
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32 cm × 8.0 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10−5N (see the following figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find (a) this constant speed, (b) the emf induced in the loop, (c) the potential difference between the points aand b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
A conducting wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m starts sliding at t = 0 down a smooth, vertical, thick pair of connected rails as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. (a) Write the induced emf in the loop at an instant t when the speed of the wire is v. (b) What would be the magnitude and direction of the induced current in the wire? (c) Find the downward acceleration of the wire at this instant. (d) After sufficient time, the wire starts moving with a constant velocity. Find this velocity vm. (e) Find the velocity of the wire as a function of time. (f) Find the displacement of the wire as a function of time. (g) Show that the rate of heat developed in the wire is equal to the rate at which the gravitational potential energy is decreased after steady state is reached.
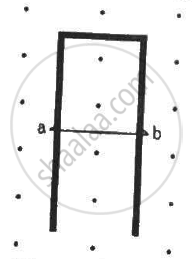
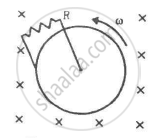
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
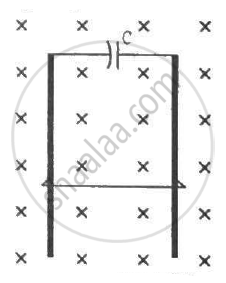
A wire of mass m and length l can slide freely on a pair of smooth, vertical rails (figure). A magnetic field B exists in the region in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. The rails are connected at the top end by a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the acceleration of the wire neglecting any electric resistance.
An inductor-coil of inductance 20 mH having resistance 10 Ω is joined to an ideal battery of emf 5.0 V. Find the rate of change of the induced emf at (a) t = 0, (b) t = 10 ms and (c) t = 1.0 s.
The mutual inductance between two coils is 2.5 H. If the current in one coil is changed at the rate of 1 As−1, what will be the emf induced in the other coil?
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance ______.
