Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
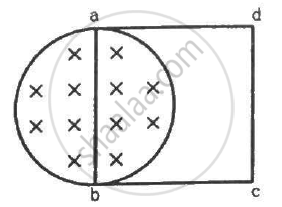
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10 cm as shown in figure. A uniform wire of length 80 cm and resistance 4.0 Ω is bent into a square frame and is placed with one side along a diameter of the cylindrical region. If the magnetic field increases at a constant rate of 0.010 T/s, find the current induced in the frame.
उत्तर
The magnetic field lines pass through coil abcd only in the part above the cylindrical region.
Radius of the cylindrical region, r = 10 cm
Resistance of the coil, R = 4 Ω
The rate of change of the magnetic field in the cylindrical region is constant and is given by
\[\frac{dB}{dt} = 0 . 010 T/s\]
The change in the magnetic flux is given by
\[\frac{d\phi}{dt} = \frac{dB}{dt}A\]
The induced emf is given by
\[e = \frac{d\phi}{dt} = \frac{dB}{dt} \times A = 0 . 01\left( \frac{\pi \times r^2}{2} \right)\]
\[ = \frac{0 . 01 \times 3 . 14 \times 0 . 01}{2}\]
\[ = \frac{3 . 14}{2} \times {10}^{- 4} = 1 . 57 \times {10}^{- 4} V\]
The current in the coil is given by
\[i = \frac{e}{R} = \frac{1 . 57 \times {10}^{- 4}}{4}\]
\[ = 0 . 39 \times {10}^{- 4} \]
\[ = 3 . 9 \times {10}^{- 5} A\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A square loop of side 12 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is moved with a velocity of 8 cm s−1 in the positive x-direction in an environment containing a magnetic field in the positive z-direction. The field is neither uniform in space nor constant in time. It has a gradient of 10−3 T cm−1 along the negative x-direction (that is it increases by 10− 3 T cm−1 as one move in the negative x-direction), and it is decreasing in time at the rate of 10−3 T s−1. Determine the direction and magnitude of the induced current in the loop if its resistance is 4.50 mΩ.
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
State Lenz’s Law.
A metallic rod held horizontally along east-west direction, is allowed to fall under gravity. Will there be an emf induced at its ends? Justify your answer.
A metallic rod of length ‘l’ is rotated with a frequency v with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius r, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is present everywhere. Using Lorentz force, explain how emf is induced between the centre and the metallic ring and hence obtained the expression for it.
A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
A conducting circular loop having a radius of 5.0 cm, is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.50 T. It is removed from the field in 0.50 s. Find the average emf produced in the loop during this time.
A square-shaped copper coil has edges of length 50 cm and contains 50 turns. It is placed perpendicular to a 1.0 T magnetic field. It is removed from the magnetic field in 0.25 s and restored in its original place in the next 0.25 s. Find the magnitude of the average emf induced in the loop during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
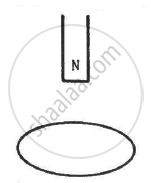
The north pole of a magnet is brought down along the axis of a horizontal circular coil (see the following figure). As a result, the flux through the coil changes from 0.35 weber to 0.85 weber in an interval of half a second. Find the average emf induced during this period. Is the induced current clockwise or anticlockwise as you look into the coil from the side of the magnet ?
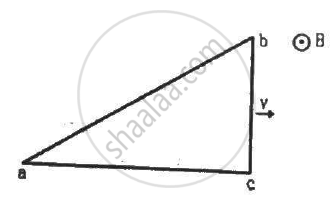
A right-angled triangle abc, made from a metallic wire, moves at a uniform speed v in its plane as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the perpendicular direction. Find the emf induced (a) in the loop abc, (b) in the segment bc, (c) in the segment ac and (d) in the segment ab.
A wire of length 10 cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60° with its length. The plane of motion is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T that exists in the space. Find the emf induced between the ends of the rod if the speed of translation is 20 cm s−1.
A rod of length l rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the two ends of the rod is ___________ .
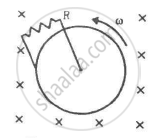
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
The current in a solenoid of 240 turns, having a length of 12 cm and a radius of 2 cm, changes at a rate of 0.8 A s−1. Find the emf induced in it.
A rectangular loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is stationary in a uniform magnetic field directed normal to the loop. The magnetic field is reduced from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s-1 If the cut is joined and loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω, then how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat?
