Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
पर्याय
clockwise
anticlockwise
zero
clockwise or anticlockwise depending on whether the resistance is increased or decreased
उत्तर
Zero
The magnetic field inside the solenoid is parallel to its axis. If the plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid, then the angle between the area vector of the circular loop and the magnetic field is zero. Thus, the flux through the circular loop is given by
`phi=BAcos theta=BA cos0^circ=BA`
Here,
B = Magnetic field due to the solenoid
A = Area of the circular loop
θ = Angle between the magnetic field and the area vector
Now, the induced emf is given by
`e=-(dphi)/(dt)`
`because varphi=BA="constant"`
∴ e = 0
We can see that the induced emf does not depend on the varying current through the solenoid and is zero for constant flux through the loop. Because there is no induced emf, no current is induced in the loop.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
(a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Calculate the average induced emf in a conducting loop of area 2.0 × 10−3 m2 placed perpendicular to the field in each of the 10 ms intervals shown. (b) In which intervals is the emf not constant? Neglect the behaviour near the ends of 10 ms intervals.
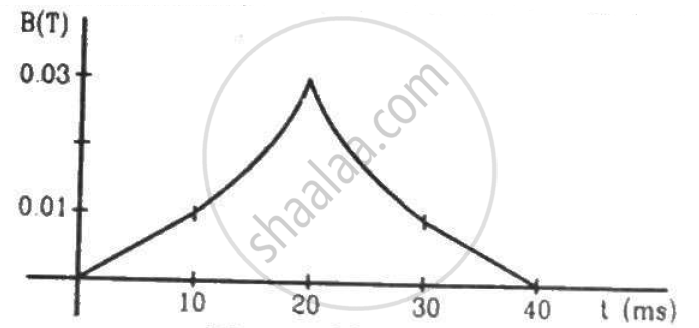
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A wire-loop confined in a plane is rotated in its own plane with some angular velocity. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. Find the emf induced in the loop.
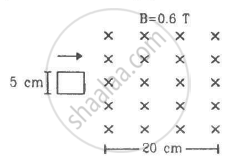
Figure shows a square loop of side 5 cm being moved towards right at a constant speed of 1 cm/s. The front edge enters the 20 cm wide magnetic field at t = 0. Find the emf induced in the loop at (a) t = 2 s, (b) t = 10 s, (c) t = 22 s and (d) t = 30 s.
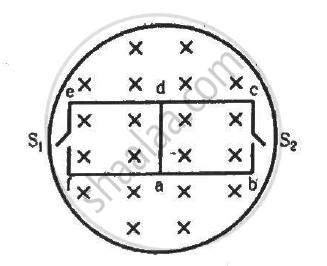
The magnetic field in the cylindrical region shown in figure increases at a constant rate of 20.0 mT/s. Each side of the square loop abcd and defa has a length of 1.00 cm and a resistance of 4.00 Ω. Find the current (magnitude and sense) in the wire ad if (a) the switch S1 is closed but S2 is open, (b) S1 is open but S2 is closed, (c) both S1 and S2 are open and (d) both S1 and S2 are closed.
A circular coil of radius 2.00 cm has 50 turns. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.200 T exists in the space in a direction parallel to the axis of the loop. The coil is now rotated about a diameter through an angle of 60.0°. The operation takes 0.100 s. (a) Find the average emf induced in the coil. (b) If the coil is a closed one (with the two ends joined together) and has a resistance of 4.00 Ω, calculate the net charge crossing a cross-section of the wire of the coil.
A closed coil having 100 turns is rotated in a uniform magnetic field B = 4.0 × 10−4 T about a diameter which is perpendicular to the field. The angular velocity of rotation is 300 revolutions per minute. The area of the coil is 25 cm2 and its resistance is 4.0 Ω. Find (a) the average emf developed in half a turn from a position where the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field, (b) the average emf in a full turn and (c) the net charge displaced in part (a).
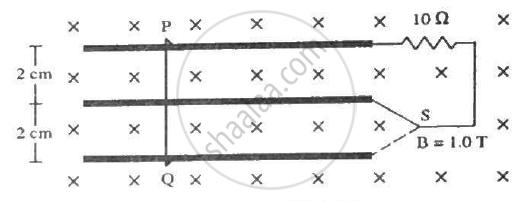
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire PQ has a negligible resistance and is made to slide on the three rails with a constant speed of 5 cm s−1. Find the current in the 10 Ω resistor when the switch S is thrown to (a) the middle rail (b) the bottom rail.
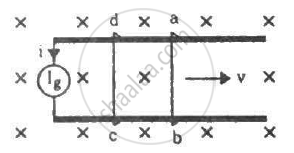
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire cd is fixed and ab is made to slide on the smooth, thick rails with a constant velocity v towards right. Each of these wires has resistance r. Find the current through the wire cd.
A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east-west direction and the rear wheel is rotated at an angular speed of 100 revolutions per minute. If the length of each spoke is 30.0 cm and the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 2.0 × 10−5 T, find the emf induced between the axis and the outer end of a spoke. Neglect centripetal force acting on the free electrons of the spoke.
The magnetic field in a region is given by \[\overrightarrow{B} = \overrightarrow{k} \frac{B_0}{L}y\] where L is a fixed length. A conducting rod of length L lies along the Y-axis between the origin and the point (0, L, 0). If the rod moves with a velocity v = v0 \[\overrightarrow{i},\] find the emf induced between the ends of the rod.
Consider a situation similar to that of the previous problem except that the ends of the rod slide on a pair of thick metallic rails laid parallel to the wire. At one end the rails are connected by resistor of resistance R. (a) What force is needed to keep the rod sliding at a constant speed v? (b) In this situation what is the current in the resistance R? (c) Find the rate of heat developed in the resistor. (d) Find the power delivered by the external agent exerting the force on the rod.
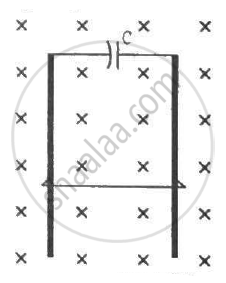
Figure shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current i given by i = i0 sin ωt. Find (a) the flux of the magnetic field through the square frame, (b) the emf induced in the frame and (c) the heat developed in the frame in the time interval 0 to \[\frac{20\pi}{\omega}.\]
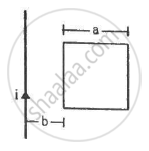
A wire of mass m and length l can slide freely on a pair of smooth, vertical rails (figure). A magnetic field B exists in the region in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. The rails are connected at the top end by a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the acceleration of the wire neglecting any electric resistance.
A current carrying infinitely long wire is kept along the diameter of a circular wire loop, without touching it, the correct statement(s) is(are)
- The emf induced in the loop is zero if the current is constant.
- The emf induced in the loop is finite if the current is constant.
- The emf induced in the loop is zero if the current decreases at a steady rate.
Two identical coaxial coils P and Q carrying equal amount of current in the same direction are brought nearer. The current in ______.
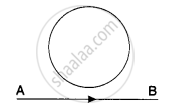
In the given figure current from A to B in the straight wire is decreasing. The direction of induced current in the loop is A ______.
A sinusoidal voltage V(t) = 100 sin (500 t) is applied across a pure inductance of L = 0.02 H. The current through the coil is:
