Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A closed coil having 100 turns is rotated in a uniform magnetic field B = 4.0 × 10−4 T about a diameter which is perpendicular to the field. The angular velocity of rotation is 300 revolutions per minute. The area of the coil is 25 cm2 and its resistance is 4.0 Ω. Find (a) the average emf developed in half a turn from a position where the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field, (b) the average emf in a full turn and (c) the net charge displaced in part (a).
उत्तर
Given:-
Number of turns in the coil, n = 100 turns
Magnetic field, B = 4 × 10−4
Area of the loop, A = 25 cm2 = 25 × 10−4 m2
(a) When the coil is perpendicular to the field:-
ϕ1 = nBA
When the coil goes through the half turn:-
ϕ2 = nBA cos 180° = −nBA
∴ Δϕ = 2nBA
When the coil undergoes 300 revolutions in 1 minute, the angle swept by the coil is
300 × 2π rad/min = 10π rad/s
10π rad is swept in 1 s.
π rad is swept in
\[\left( \frac{1}{10\pi} \right)\pi = \frac{1}{10} s\]
\[e = \frac{d\phi}{dt} = \frac{2nBA}{dt}\]
\[ = \frac{2 \times 100 \times 4 \times {10}^{- 4} \times 25 \times {10}^{- 4}}{1/10}\]
\[ = 2 \times {10}^{- 3} V\]
(b) ϕ1 = nBA, ϕ2 = nBA (θ = 360°)
Δϕ = 0, thus emf induced will be zero.
(c) The current flowing in the coil is given by
\[i = \frac{e}{R} = \frac{2 \times {10}^{- 3}}{4} = \frac{1}{2} \times {10}^{- 3}\]
= 0.5 × 10−3 = 5 × 10−4 A
Hence, the net charge is given by
Q = idt = 5 × 10−4 × `1/10`
= 5 × 10−5 C
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expression for the (i) emf and (ii) internal resistance of a single equivalent cell which can replace this combination.
(a) Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance between a long straight wire and a square loop of side an as shown in the figure.
(b) Now assume that the straight wire carries a current of 50 A and the loop is moved to the right with a constant velocity, v = 10 m/s.
Calculate the induced emf in the loop at the instant when x = 0.2 m.
Take a = 0.1 m and assume that the loop has a large resistance.

An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
Two circular loops are placed coaxially but separated by a distance. A battery is suddenly connected to one of the loops establishing a current in it. Will there be a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does the current start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or do they repel?
Consider the following statements:-
(A) An emf can be induced by moving a conductor in a magnetic field.
(B) An emf can be induced by changing the magnetic field.
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire AB is slid on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by a semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will _____________ .

An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
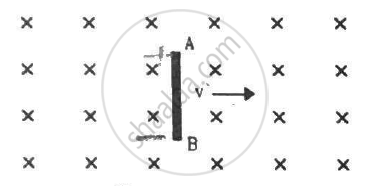
A rod AB moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure.
A conducting circular loop of area 1 mm2 is placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire at a distance of 20 cm from it. The straight wire carries an electric current which changes from 10 A to zero in 0.1 s. Find the average emf induced in the loop in 0.1 s.
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A circular coil of one turn of radius 5.0 cm is rotated about a diameter with a constant angular speed of 80 revolutions per minute. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.010 T exists in a direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Find (a) the maximum emf induced, (b) the average emf induced in the coil over a long period and (c) the average of the squares of emf induced over a long period.
A circular copper-ring of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the ring. Consider different pairs of diametrically opposite points on the ring. (a) Between which pair of points is the emf maximum? What is the value of this maximum emf? (b) Between which pair of points is the emf minimum? What is the value of this minimum emf ?
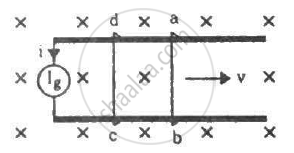
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire cd is fixed and ab is made to slide on the smooth, thick rails with a constant velocity v towards right. Each of these wires has resistance r. Find the current through the wire cd.
Consider a situation similar to that of the previous problem except that the ends of the rod slide on a pair of thick metallic rails laid parallel to the wire. At one end the rails are connected by resistor of resistance R. (a) What force is needed to keep the rod sliding at a constant speed v? (b) In this situation what is the current in the resistance R? (c) Find the rate of heat developed in the resistor. (d) Find the power delivered by the external agent exerting the force on the rod.
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region, shown dotted in figure. The magnetic field increases at a constant rate `(dB)/(dt).` Consider a circle of radius r coaxial with the cylindrical region. (a) Find the magnitude of the electric field E at a point on the circumference of the circle. (b) Consider a point P on the side of the square circumscribing the circle. Show that the component of the induced electric field at P along ba is the same as the magnitude found in part (a).

In the given figure current from A to B in the straight wire is decreasing. The direction of induced current in the loop is A ______.
The current flowing in a step-down transformer 220 V to 22 V having impedance 220 π is
