Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
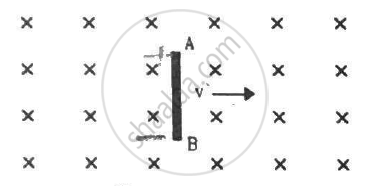
A rod AB moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure.
पर्याय
The rod becomes electrically charged
The end A becomes positively charged
The end B becomes positively charged.
The rod becomes hot because of Joule heating
उत्तर
The end A becomes positively charged
Due to electromagnetic induction, emf e is induced across the ends of the rod. This induced emf is given by
`e=Bvl`
The direction of this induced emf is from A to B, that is, A is at the higher potential and B is at the lower potential. This is because the magnetic field exerts a force equal to `qvB` on each free electron where q is -1.6 × 10-16C. The force is towards AB by Fleming's left-hand rule; hence, negatively charged electrons move towards the end B and get accumulated near it. So, a negative charge appears at B and a positive charge appears at A.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The current flowing through an inductor of self-inductance L is continuously increasing. Plot a graph showing the variation of
Induced emf versus dI/dt
A square loop of side 12 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is moved with a velocity of 8 cm s−1 in the positive x-direction in an environment containing a magnetic field in the positive z-direction. The field is neither uniform in space nor constant in time. It has a gradient of 10−3 T cm−1 along the negative x-direction (that is it increases by 10− 3 T cm−1 as one move in the negative x-direction), and it is decreasing in time at the rate of 10−3 T s−1. Determine the direction and magnitude of the induced current in the loop if its resistance is 4.50 mΩ.
A metallic rod of ‘L’ length is rotated with angular frequency of ‘ω’ with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius L, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is presents everywhere. Deduce the expression for the emf between the centre and the metallic ring.
An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
(a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Calculate the average induced emf in a conducting loop of area 2.0 × 10−3 m2 placed perpendicular to the field in each of the 10 ms intervals shown. (b) In which intervals is the emf not constant? Neglect the behaviour near the ends of 10 ms intervals.
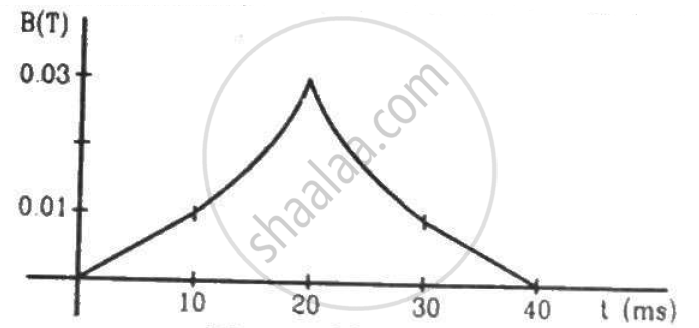
Figure shows a conducting square loop placed parallel to the pole-faces of a ring magnet. The pole-faces have an area of 1 cm2 each and the field between the poles is 0.10 T. The wires making the loop are all outside the magnetic field. If the magnet is removed in 1.0 s, what is the average emf induced in the loop?
A copper wire bent in the shape of a semicircle of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the emf induced between the ends of the wire if (a) the velocity is perpendicular to the diameter joining free ends, (b) the velocity is parallel to this diameter.
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire PQ has a negligible resistance and is made to slide on the three rails with a constant speed of 5 cm s−1. Find the current in the 10 Ω resistor when the switch S is thrown to (a) the middle rail (b) the bottom rail.
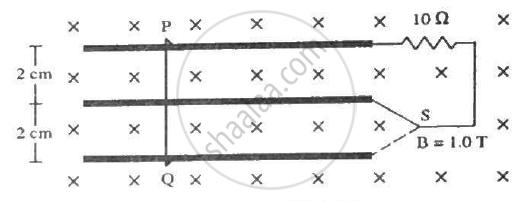
Figure shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current i given by i = i0 sin ωt. Find (a) the flux of the magnetic field through the square frame, (b) the emf induced in the frame and (c) the heat developed in the frame in the time interval 0 to \[\frac{20\pi}{\omega}.\]
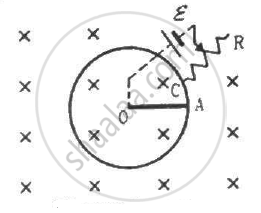
Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. A battery of emf ε and a variable resistance R are connected between O and C. Neglect the resistance of the connecting wires. Let θ be the angle made by the rod from the horizontal position (show in the figure), measured in the clockwise direction. During the part of the motion 0 < θ < π/4 the only forces acting on the rod are gravity and the forces exerted by the magnetic field and the pivot. However, during the part of the motion, the resistance R is varied in such a way that the rod continues to rotate with a constant angular velocity ω. Find the value of R in terms of the given quantities.
An inductor-coil of inductance 20 mH having resistance 10 Ω is joined to an ideal battery of emf 5.0 V. Find the rate of change of the induced emf at (a) t = 0, (b) t = 10 ms and (c) t = 1.0 s.
Plot a graph showing variation of induced e.m.f. with the rate of change of current flowing through a coil.
An induced e.m.f. is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. The strength of the induced e.m.f. is independent of ______.
A rectangular loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is stationary in a uniform magnetic field directed normal to the loop. The magnetic field is reduced from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s-1 If the cut is joined and loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω, then how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat?
