Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows a conducting square loop placed parallel to the pole-faces of a ring magnet. The pole-faces have an area of 1 cm2 each and the field between the poles is 0.10 T. The wires making the loop are all outside the magnetic field. If the magnet is removed in 1.0 s, what is the average emf induced in the loop?
उत्तर
It is given that the magnitude of the magnetic field is 0.10 T and it is perpendicular to the area of the loop.
Also,
Area of the loop, A = 1 cm2 = 10−4 m
Time taken to remove the magnet completely, T = 2 s
Initial magnetic flux, ϕ = \[\overrightarrow{B} . \overrightarrow{A}\] = BA cos(0) = 10−1 × 10−4 × 1 = 10−5
Now, the induced emf in the magnetic field is given by
\[e = - \frac{∆ \phi}{∆ t} = \frac{{10}^{- 5} - 0}{1} = {10}^{- 5} = 10 \mu V\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutual perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of the closed loop containing the rod = 9.0 mΩ. Assume the field to be uniform.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod is moved with a speed of 12 cm s−1 in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of the induced emf.
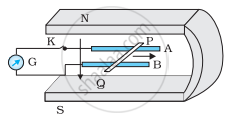
(b) Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rods when K is open? What if K is closed?
(c) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electrons in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic force due to the motion of the rod. Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much power is required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed = (12 cm s−1) when K is closed? How much power is required when K is open?
(f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced emf in the moving rod if the magnetic field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular?
A rectangular coil of area A, having the number of turns N is rotated at 'f' revolutions per second in a uniform magnetic field B, the field being perpendicular to the coil. Prove that the maximum emf induced in the coil is 2 πf NBA.
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire AB is slid on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by a semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will _____________ .

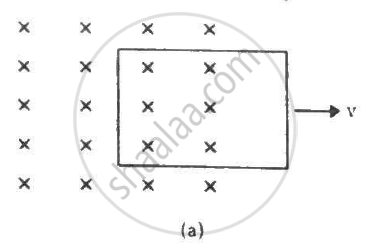
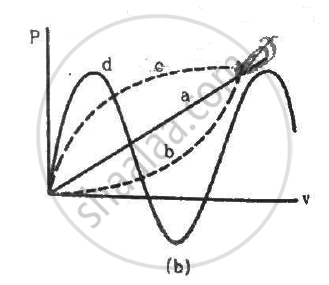
Figure shows a conducting loop being pulled out of a magnetic field with a speed v. Which of the four plots shown in figure (b) may represent the power delivered by the pulling agent as a function of the speed v?
A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
A rod AB moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure.
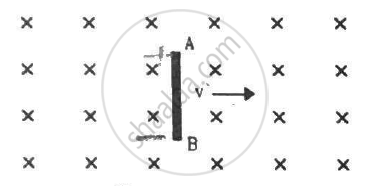
(a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Calculate the average induced emf in a conducting loop of area 2.0 × 10−3 m2 placed perpendicular to the field in each of the 10 ms intervals shown. (b) In which intervals is the emf not constant? Neglect the behaviour near the ends of 10 ms intervals.
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A right-angled triangle abc, made from a metallic wire, moves at a uniform speed v in its plane as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the perpendicular direction. Find the emf induced (a) in the loop abc, (b) in the segment bc, (c) in the segment ac and (d) in the segment ab.
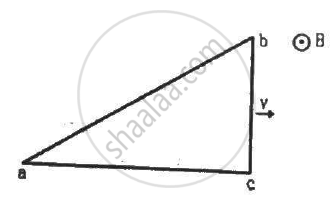
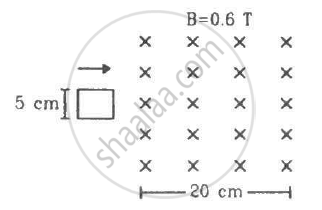
Figure shows a square loop of side 5 cm being moved towards right at a constant speed of 1 cm/s. The front edge enters the 20 cm wide magnetic field at t = 0. Find the total heat produced in the loop during the interval 0 to 30 s if the resistance of the loop is 4.5 mΩ.
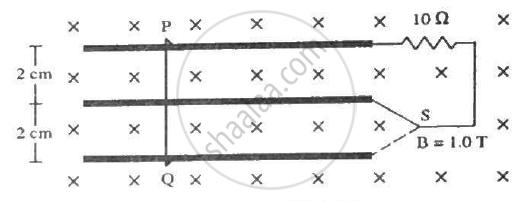
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire PQ has a negligible resistance and is made to slide on the three rails with a constant speed of 5 cm s−1. Find the current in the 10 Ω resistor when the switch S is thrown to (a) the middle rail (b) the bottom rail.
The magnetic field in a region is given by \[\overrightarrow{B} = \overrightarrow{k} \frac{B_0}{L}y\] where L is a fixed length. A conducting rod of length L lies along the Y-axis between the origin and the point (0, L, 0). If the rod moves with a velocity v = v0 \[\overrightarrow{i},\] find the emf induced between the ends of the rod.
An inductor-coil of inductance 20 mH having resistance 10 Ω is joined to an ideal battery of emf 5.0 V. Find the rate of change of the induced emf at (a) t = 0, (b) t = 10 ms and (c) t = 1.0 s.
The mutual inductance between two coils is 2.5 H. If the current in one coil is changed at the rate of 1 As−1, what will be the emf induced in the other coil?
An alternating emf of 110 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance R of 80 Ω and an inductor L in series. The current is found to lag behind the supply voltage by an angle 8 = tan-1 (3/4). Find the :
(i) Inductive reactance
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
(iii) Current flowing in the circuit
(iv) If the inductor has a coefficient of self-inductance of 0.1 H, what is the frequency of the applied emf?
Two identical coaxial coils P and Q carrying equal amount of current in the same direction are brought nearer. The current in ______.
