Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
उत्तर
Given:-
Resistance of the coil, R = 25 Ω
(a) During the removal the emf induced in the coil,
e = 50 V
time taken, t = 0.25 s
current in the coil,
\[i = \frac{e}{R} = 2A\]
Thus, the thermal energy developed is given by
H = I2RT
= 4 × 25 × 0.25 = 25 J
(b) During the restoration of the coil,
emf induced in it, e = 50 V
time taken, t = 0.25 s
current in the coil,
\[i = \frac{e}{R} = 2A\]
Thus, the thermal energy developed is given by
H = i2RT = 25 J
(c) We know that energy is a scalar quantity. Also, the net thermal energy is the algebraic sum of the two energies calculated.
∴ Net thermal energy developed
= 25 J + 25 J = 50 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expression for the (i) emf and (ii) internal resistance of a single equivalent cell which can replace this combination.
Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutual perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of the closed loop containing the rod = 9.0 mΩ. Assume the field to be uniform.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod is moved with a speed of 12 cm s−1 in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of the induced emf.
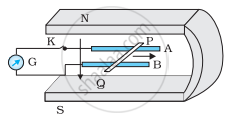
(b) Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rods when K is open? What if K is closed?
(c) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electrons in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic force due to the motion of the rod. Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much power is required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed = (12 cm s−1) when K is closed? How much power is required when K is open?
(f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced emf in the moving rod if the magnetic field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular?
An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
State Lenz’s Law.
A metallic rod held horizontally along east-west direction, is allowed to fall under gravity. Will there be an emf induced at its ends? Justify your answer.
Consider the following statements:-
(A) An emf can be induced by moving a conductor in a magnetic field.
(B) An emf can be induced by changing the magnetic field.
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire AB is slid on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by a semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will _____________ .

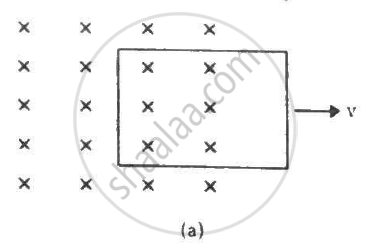
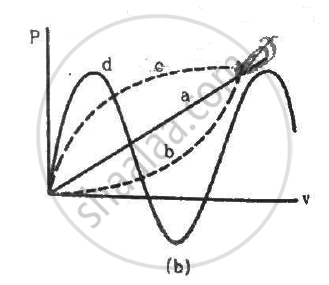
Figure shows a conducting loop being pulled out of a magnetic field with a speed v. Which of the four plots shown in figure (b) may represent the power delivered by the pulling agent as a function of the speed v?
An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
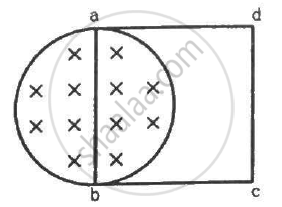
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10 cm as shown in figure. A uniform wire of length 80 cm and resistance 4.0 Ω is bent into a square frame and is placed with one side along a diameter of the cylindrical region. If the magnetic field increases at a constant rate of 0.010 T/s, find the current induced in the frame.
A circular coil of radius 2.00 cm has 50 turns. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.200 T exists in the space in a direction parallel to the axis of the loop. The coil is now rotated about a diameter through an angle of 60.0°. The operation takes 0.100 s. (a) Find the average emf induced in the coil. (b) If the coil is a closed one (with the two ends joined together) and has a resistance of 4.00 Ω, calculate the net charge crossing a cross-section of the wire of the coil.
A metallic metre stick moves with a velocity of 2 m s−1 in a direction perpendicular to its length and perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.2 T. Find the emf induced between the ends of the stick.
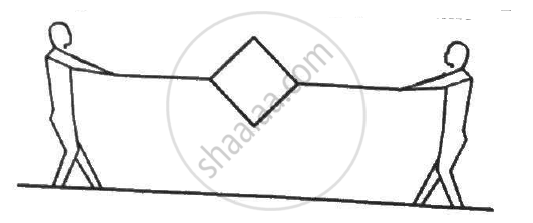
Figure shows a metallic square frame of edge a in a vertical plane. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the figure. Two boys pull the opposite corners of the square to deform it into a rhombus. They start pulling the corners at t = 0 and displace the corners at a uniform speed u. (a) Find the induced emf in the frame at the instant when the angles at these corners reduce to 60°. (b) Find the induced current in the frame at this instant if the total resistance of the frame is R. (c) Find the total charge which flows through a side of the frame by the time the square is deformed into a straight line.
A rod of length l rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the two ends of the rod is ___________ .
Figure shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current i given by i = i0 sin ωt. Find (a) the flux of the magnetic field through the square frame, (b) the emf induced in the frame and (c) the heat developed in the frame in the time interval 0 to \[\frac{20\pi}{\omega}.\]
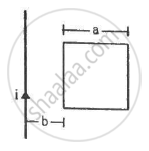
A wire of mass m and length l can slide freely on a pair of smooth, vertical rails (figure). A magnetic field B exists in the region in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. The rails are connected at the top end by a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the acceleration of the wire neglecting any electric resistance.
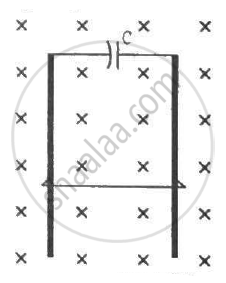
The current in a solenoid of 240 turns, having a length of 12 cm and a radius of 2 cm, changes at a rate of 0.8 A s−1. Find the emf induced in it.
A small flat search coil of area 5cm2 with 140 closely wound turns is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet producing magnetic field 0.09T and then quickly removed out of the field region. Calculate:
(a) Change of magnetic flux through the coil, and
(b) emf induced in the coil.
Plot a graph showing variation of induced e.m.f. with the rate of change of current flowing through a coil.
An induced e.m.f. is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. The strength of the induced e.m.f. is independent of ______.
A sinusoidal voltage V(t) = 100 sin (500 t) is applied across a pure inductance of L = 0.02 H. The current through the coil is:
