Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The current in a solenoid of 240 turns, having a length of 12 cm and a radius of 2 cm, changes at a rate of 0.8 A s−1. Find the emf induced in it.
उत्तर
Given:-
Number of turns, N = 240
Radius of the solenoid, r = 2 cm
Length of the solenoid, l = 12 cm
The emf induced in the solenoid is given by
The self-inductance of the solenoid is given by
Thus, the emf induced in the solenoid is given by
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular coil of area A, having the number of turns N is rotated at 'f' revolutions per second in a uniform magnetic field B, the field being perpendicular to the coil. Prove that the maximum emf induced in the coil is 2 πf NBA.
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
A metallic rod of length ‘l’ is rotated with a frequency v with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius r, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is present everywhere. Using Lorentz force, explain how emf is induced between the centre and the metallic ring and hence obtained the expression for it.
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire AB is slid on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by a semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will _____________ .

A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
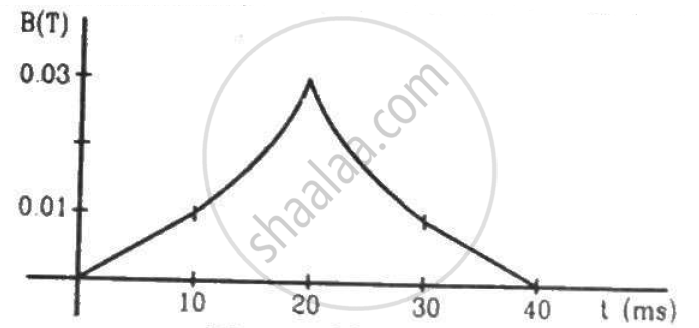
(a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Calculate the average induced emf in a conducting loop of area 2.0 × 10−3 m2 placed perpendicular to the field in each of the 10 ms intervals shown. (b) In which intervals is the emf not constant? Neglect the behaviour near the ends of 10 ms intervals.
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A conducting wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m starts sliding at t = 0 down a smooth, vertical, thick pair of connected rails as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. (a) Write the induced emf in the loop at an instant t when the speed of the wire is v. (b) What would be the magnitude and direction of the induced current in the wire? (c) Find the downward acceleration of the wire at this instant. (d) After sufficient time, the wire starts moving with a constant velocity. Find this velocity vm. (e) Find the velocity of the wire as a function of time. (f) Find the displacement of the wire as a function of time. (g) Show that the rate of heat developed in the wire is equal to the rate at which the gravitational potential energy is decreased after steady state is reached.
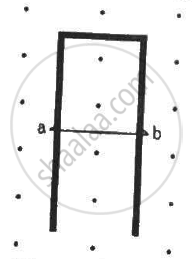
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
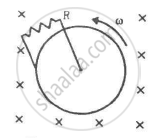
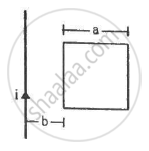
Figure shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current i given by i = i0 sin ωt. Find (a) the flux of the magnetic field through the square frame, (b) the emf induced in the frame and (c) the heat developed in the frame in the time interval 0 to
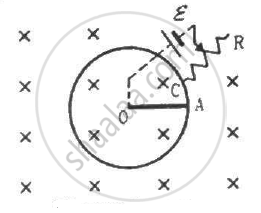
Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. A battery of emf ε and a variable resistance R are connected between O and C. Neglect the resistance of the connecting wires. Let θ be the angle made by the rod from the horizontal position (show in the figure), measured in the clockwise direction. During the part of the motion 0 < θ < π/4 the only forces acting on the rod are gravity and the forces exerted by the magnetic field and the pivot. However, during the part of the motion, the resistance R is varied in such a way that the rod continues to rotate with a constant angular velocity ω. Find the value of R in terms of the given quantities.
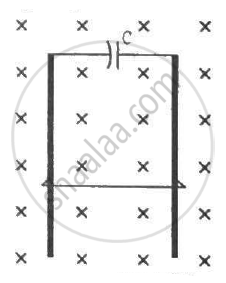
A wire of mass m and length l can slide freely on a pair of smooth, vertical rails (figure). A magnetic field B exists in the region in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. The rails are connected at the top end by a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the acceleration of the wire neglecting any electric resistance.
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region, shown dotted in figure. The magnetic field increases at a constant rate

An alternating emf of 110 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance R of 80 Ω and an inductor L in series. The current is found to lag behind the supply voltage by an angle 8 = tan-1 (3/4). Find the :
(i) Inductive reactance
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
(iii) Current flowing in the circuit
(iv) If the inductor has a coefficient of self-inductance of 0.1 H, what is the frequency of the applied emf?
A current carrying infinitely long wire is kept along the diameter of a circular wire loop, without touching it, the correct statement(s) is(are)
- The emf induced in the loop is zero if the current is constant.
- The emf induced in the loop is finite if the current is constant.
- The emf induced in the loop is zero if the current decreases at a steady rate.
When the rate of change oic current is unity, the induced emf is equal to ______.
The current flowing in a step-down transformer 220 V to 22 V having impedance 220 π is
