Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
पर्याय
Current in the circuit
Magnetic field energy in the inductor
Power delivered by the battery
Emf induced in the inductor
उत्तर
Emf induced in the inductor
At time t = 0, the current in the L-R circuit is zero. The magnetic field energy is given by `U=1/2Li^2,` as the current is zero the magnetic field energy will also be zero. Thus, the power delivered by the battery will also be zero. As, the LR circuit is connected to the battery at t = 0, at this time the current is on the verge to start growing in the circuit. So, there will be an induced emf in the inductor at the same time to oppose this growing current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance between a long straight wire and a square loop of side an as shown in the figure.
(b) Now assume that the straight wire carries a current of 50 A and the loop is moved to the right with a constant velocity, v = 10 m/s.
Calculate the induced emf in the loop at the instant when x = 0.2 m.
Take a = 0.1 m and assume that the loop has a large resistance.

An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
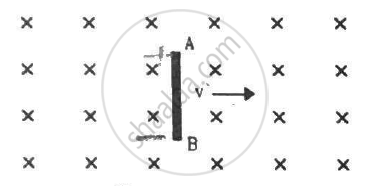
A rod AB moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure.
The flux of magnetic field through a closed conducting loop changes with time according to the equation, Φ = at2 + bt + c. (a) Write the SI units of a, b and c. (b) If the magnitudes of a, b and c are 0.20, 0.40 and 0.60 respectively, find the induced emf at t = 2 s.
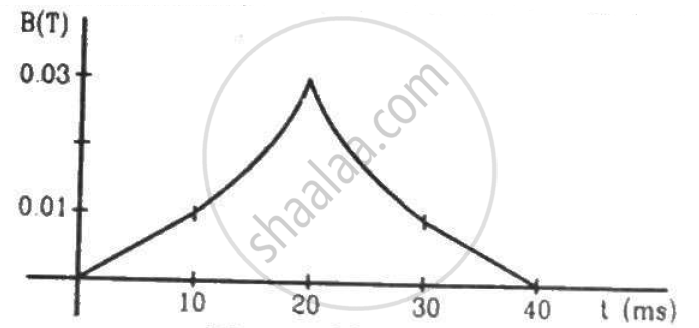
(a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Calculate the average induced emf in a conducting loop of area 2.0 × 10−3 m2 placed perpendicular to the field in each of the 10 ms intervals shown. (b) In which intervals is the emf not constant? Neglect the behaviour near the ends of 10 ms intervals.
A conducting loop of area 5.0 cm2 is placed in a magnetic field which varies sinusoidally with time as B = B0 sin ωt where B0 = 0.20 T and ω = 300 s−1. The normal to the coil makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find (a) the maximum emf induced in the coil, (b) the emf induced at τ = (π/900)s and (c) the emf induced at t = (π/600) s.
Figure shows a conducting square loop placed parallel to the pole-faces of a ring magnet. The pole-faces have an area of 1 cm2 each and the field between the poles is 0.10 T. The wires making the loop are all outside the magnetic field. If the magnet is removed in 1.0 s, what is the average emf induced in the loop?
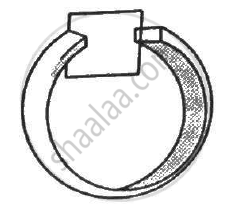
The north pole of a magnet is brought down along the axis of a horizontal circular coil (see the following figure). As a result, the flux through the coil changes from 0.35 weber to 0.85 weber in an interval of half a second. Find the average emf induced during this period. Is the induced current clockwise or anticlockwise as you look into the coil from the side of the magnet ?
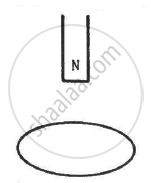
A wire-loop confined in a plane is rotated in its own plane with some angular velocity. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. Find the emf induced in the loop.
A closed coil having 100 turns is rotated in a uniform magnetic field B = 4.0 × 10−4 T about a diameter which is perpendicular to the field. The angular velocity of rotation is 300 revolutions per minute. The area of the coil is 25 cm2 and its resistance is 4.0 Ω. Find (a) the average emf developed in half a turn from a position where the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field, (b) the average emf in a full turn and (c) the net charge displaced in part (a).
A copper wire bent in the shape of a semicircle of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the emf induced between the ends of the wire if (a) the velocity is perpendicular to the diameter joining free ends, (b) the velocity is parallel to this diameter.
A wire of length 10 cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60° with its length. The plane of motion is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T that exists in the space. Find the emf induced between the ends of the rod if the speed of translation is 20 cm s−1.
A circular copper-ring of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the ring. Consider different pairs of diametrically opposite points on the ring. (a) Between which pair of points is the emf maximum? What is the value of this maximum emf? (b) Between which pair of points is the emf minimum? What is the value of this minimum emf ?
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32 cm × 8.0 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10−5N (see the following figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find (a) this constant speed, (b) the emf induced in the loop, (c) the potential difference between the points aand b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
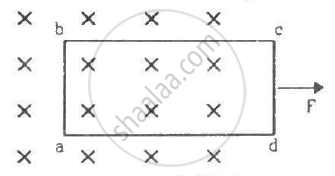
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
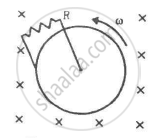
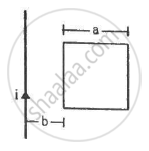
Figure shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current i given by i = i0 sin ωt. Find (a) the flux of the magnetic field through the square frame, (b) the emf induced in the frame and (c) the heat developed in the frame in the time interval 0 to \[\frac{20\pi}{\omega}.\]
When the rate of change oic current is unity, the induced emf is equal to ______.
