Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
विकल्प
Current in the circuit
Magnetic field energy in the inductor
Power delivered by the battery
Emf induced in the inductor
उत्तर
Emf induced in the inductor
At time t = 0, the current in the L-R circuit is zero. The magnetic field energy is given by `U=1/2Li^2,` as the current is zero the magnetic field energy will also be zero. Thus, the power delivered by the battery will also be zero. As, the LR circuit is connected to the battery at t = 0, at this time the current is on the verge to start growing in the circuit. So, there will be an induced emf in the inductor at the same time to oppose this growing current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A square loop of side 12 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is moved with a velocity of 8 cm s−1 in the positive x-direction in an environment containing a magnetic field in the positive z-direction. The field is neither uniform in space nor constant in time. It has a gradient of 10−3 T cm−1 along the negative x-direction (that is it increases by 10− 3 T cm−1 as one move in the negative x-direction), and it is decreasing in time at the rate of 10−3 T s−1. Determine the direction and magnitude of the induced current in the loop if its resistance is 4.50 mΩ.
Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutual perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of the closed loop containing the rod = 9.0 mΩ. Assume the field to be uniform.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod is moved with a speed of 12 cm s−1 in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of the induced emf.
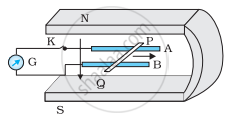
(b) Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rods when K is open? What if K is closed?
(c) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electrons in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic force due to the motion of the rod. Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much power is required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed = (12 cm s−1) when K is closed? How much power is required when K is open?
(f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced emf in the moving rod if the magnetic field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular?
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
A square-shaped copper coil has edges of length 50 cm and contains 50 turns. It is placed perpendicular to a 1.0 T magnetic field. It is removed from the magnetic field in 0.25 s and restored in its original place in the next 0.25 s. Find the magnitude of the average emf induced in the loop during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A conducting loop of area 5.0 cm2 is placed in a magnetic field which varies sinusoidally with time as B = B0 sin ωt where B0 = 0.20 T and ω = 300 s−1. The normal to the coil makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find (a) the maximum emf induced in the coil, (b) the emf induced at τ = (π/900)s and (c) the emf induced at t = (π/600) s.
A wire-loop confined in a plane is rotated in its own plane with some angular velocity. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. Find the emf induced in the loop.
A circular coil of one turn of radius 5.0 cm is rotated about a diameter with a constant angular speed of 80 revolutions per minute. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.010 T exists in a direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Find (a) the maximum emf induced, (b) the average emf induced in the coil over a long period and (c) the average of the squares of emf induced over a long period.
A copper wire bent in the shape of a semicircle of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the emf induced between the ends of the wire if (a) the velocity is perpendicular to the diameter joining free ends, (b) the velocity is parallel to this diameter.
Figure shows a metallic square frame of edge a in a vertical plane. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the figure. Two boys pull the opposite corners of the square to deform it into a rhombus. They start pulling the corners at t = 0 and displace the corners at a uniform speed u. (a) Find the induced emf in the frame at the instant when the angles at these corners reduce to 60°. (b) Find the induced current in the frame at this instant if the total resistance of the frame is R. (c) Find the total charge which flows through a side of the frame by the time the square is deformed into a straight line.
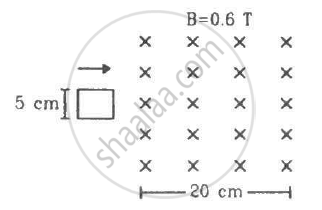
Figure shows a square loop of side 5 cm being moved towards right at a constant speed of 1 cm/s. The front edge enters the 20 cm wide magnetic field at t = 0. Find the total heat produced in the loop during the interval 0 to 30 s if the resistance of the loop is 4.5 mΩ.
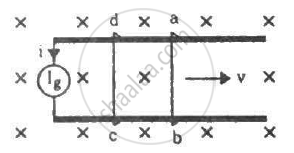
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire cd is fixed and ab is made to slide on the smooth, thick rails with a constant velocity v towards right. Each of these wires has resistance r. Find the current through the wire cd.
A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east-west direction and the rear wheel is rotated at an angular speed of 100 revolutions per minute. If the length of each spoke is 30.0 cm and the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 2.0 × 10−5 T, find the emf induced between the axis and the outer end of a spoke. Neglect centripetal force acting on the free electrons of the spoke.
Figure shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current i given by i = i0 sin ωt. Find (a) the flux of the magnetic field through the square frame, (b) the emf induced in the frame and (c) the heat developed in the frame in the time interval 0 to \[\frac{20\pi}{\omega}.\]
An alternating emf of 110 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance R of 80 Ω and an inductor L in series. The current is found to lag behind the supply voltage by an angle 8 = tan-1 (3/4). Find the :
(i) Inductive reactance
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
(iii) Current flowing in the circuit
(iv) If the inductor has a coefficient of self-inductance of 0.1 H, what is the frequency of the applied emf?
Plot a graph showing variation of induced e.m.f. with the rate of change of current flowing through a coil.
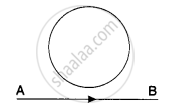
In the given figure current from A to B in the straight wire is decreasing. The direction of induced current in the loop is A ______.
A sinusoidal voltage V(t) = 100 sin (500 t) is applied across a pure inductance of L = 0.02 H. The current through the coil is:
The current flowing in a step-down transformer 220 V to 22 V having impedance 220 π is
