Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
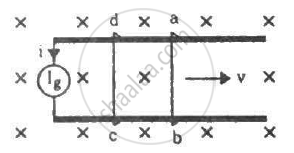
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire cd is fixed and ab is made to slide on the smooth, thick rails with a constant velocity v towards right. Each of these wires has resistance r. Find the current through the wire cd.
उत्तर
Current passing through the circuit initially = i
Initial emf = ir
Emf induced due to motion of ab, e = Blv
Net emf, enet= ir − Blv
Net resistance = 2r
Thus, the current passing through the circuit is `(ir-Blv)/(2r)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expression for the (i) emf and (ii) internal resistance of a single equivalent cell which can replace this combination.
(a) Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance between a long straight wire and a square loop of side an as shown in the figure.
(b) Now assume that the straight wire carries a current of 50 A and the loop is moved to the right with a constant velocity, v = 10 m/s.
Calculate the induced emf in the loop at the instant when x = 0.2 m.
Take a = 0.1 m and assume that the loop has a large resistance.

An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
State Lenz’s Law.
A metallic rod held horizontally along east-west direction, is allowed to fall under gravity. Will there be an emf induced at its ends? Justify your answer.
Consider the following statements:-
(A) An emf can be induced by moving a conductor in a magnetic field.
(B) An emf can be induced by changing the magnetic field.
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire AB is slid on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by a semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will _____________ .

The flux of magnetic field through a closed conducting loop changes with time according to the equation, Φ = at2 + bt + c. (a) Write the SI units of a, b and c. (b) If the magnitudes of a, b and c are 0.20, 0.40 and 0.60 respectively, find the induced emf at t = 2 s.
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A circular coil of radius 2.00 cm has 50 turns. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.200 T exists in the space in a direction parallel to the axis of the loop. The coil is now rotated about a diameter through an angle of 60.0°. The operation takes 0.100 s. (a) Find the average emf induced in the coil. (b) If the coil is a closed one (with the two ends joined together) and has a resistance of 4.00 Ω, calculate the net charge crossing a cross-section of the wire of the coil.
A right-angled triangle abc, made from a metallic wire, moves at a uniform speed v in its plane as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the perpendicular direction. Find the emf induced (a) in the loop abc, (b) in the segment bc, (c) in the segment ac and (d) in the segment ab.
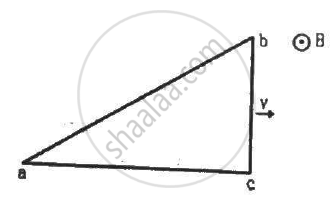
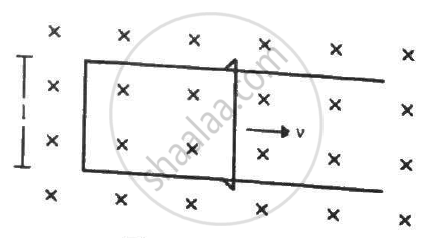
Figure shows a long U-shaped wire of width l placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A wire of length l is slid on the U-shaped wire with a constant velocity v towards right. The resistance of all the wires is r per unit length. At t = 0, the sliding wire is close to the left edge of the U-shaped wire. Draw an equivalent circuit diagram, showing the induced emf as a battery. Calculate the current in the circuit.
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32 cm × 8.0 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10−5N (see the following figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find (a) this constant speed, (b) the emf induced in the loop, (c) the potential difference between the points aand b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
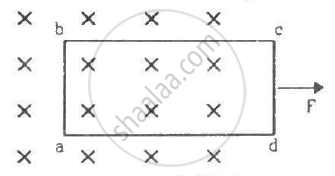
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
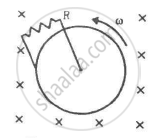
Consider a situation similar to that of the previous problem except that the ends of the rod slide on a pair of thick metallic rails laid parallel to the wire. At one end the rails are connected by resistor of resistance R. (a) What force is needed to keep the rod sliding at a constant speed v? (b) In this situation what is the current in the resistance R? (c) Find the rate of heat developed in the resistor. (d) Find the power delivered by the external agent exerting the force on the rod.
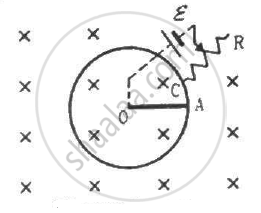
Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. A battery of emf ε and a variable resistance R are connected between O and C. Neglect the resistance of the connecting wires. Let θ be the angle made by the rod from the horizontal position (show in the figure), measured in the clockwise direction. During the part of the motion 0 < θ < π/4 the only forces acting on the rod are gravity and the forces exerted by the magnetic field and the pivot. However, during the part of the motion, the resistance R is varied in such a way that the rod continues to rotate with a constant angular velocity ω. Find the value of R in terms of the given quantities.
A rectangular loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is stationary in a uniform magnetic field directed normal to the loop. The magnetic field is reduced from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s-1 If the cut is joined and loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω, then how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat?
