Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A wire of length 10 cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60° with its length. The plane of motion is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T that exists in the space. Find the emf induced between the ends of the rod if the speed of translation is 20 cm s−1.
उत्तर
Given:-
Length of the rod, l = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Angle between the velocity and length of the rod, θ = 60°
Magnetic field, B = 1 T
Velocity of the rod, v = 20 cm/s = 0.2 m/s
The motional emf induced in the rod is given by
\[e = \left( \overrightarrow{v} \times \overrightarrow{B} \right) . \overrightarrow{l}\]
∴ e = Bvl sin 60°
We take the component of the length vector that is perpendicular to the velocity vector.
\[\therefore e=1 \times 0 . 2 \times 0 . 1 \times \sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}\]
= 17.32 × 10−3 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expression for the (i) emf and (ii) internal resistance of a single equivalent cell which can replace this combination.
The current flowing through an inductor of self-inductance L is continuously increasing. Plot a graph showing the variation of
Induced emf versus dI/dt
Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutual perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of the closed loop containing the rod = 9.0 mΩ. Assume the field to be uniform.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod is moved with a speed of 12 cm s−1 in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of the induced emf.
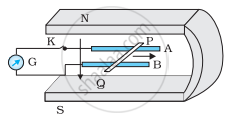
(b) Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rods when K is open? What if K is closed?
(c) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electrons in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic force due to the motion of the rod. Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much power is required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed = (12 cm s−1) when K is closed? How much power is required when K is open?
(f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced emf in the moving rod if the magnetic field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular?
(a) Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance between a long straight wire and a square loop of side an as shown in the figure.
(b) Now assume that the straight wire carries a current of 50 A and the loop is moved to the right with a constant velocity, v = 10 m/s.
Calculate the induced emf in the loop at the instant when x = 0.2 m.
Take a = 0.1 m and assume that the loop has a large resistance.

What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
Two circular loops are placed coaxially but separated by a distance. A battery is suddenly connected to one of the loops establishing a current in it. Will there be a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does the current start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or do they repel?
(a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Calculate the average induced emf in a conducting loop of area 2.0 × 10−3 m2 placed perpendicular to the field in each of the 10 ms intervals shown. (b) In which intervals is the emf not constant? Neglect the behaviour near the ends of 10 ms intervals.
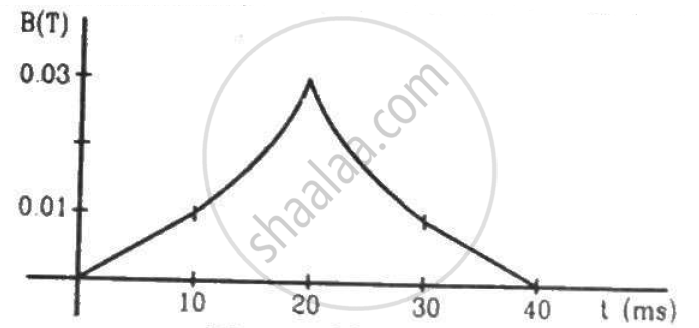
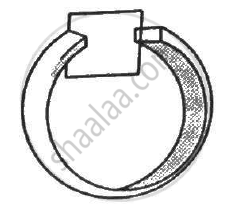
Figure shows a conducting square loop placed parallel to the pole-faces of a ring magnet. The pole-faces have an area of 1 cm2 each and the field between the poles is 0.10 T. The wires making the loop are all outside the magnetic field. If the magnet is removed in 1.0 s, what is the average emf induced in the loop?
A closed coil having 100 turns is rotated in a uniform magnetic field B = 4.0 × 10−4 T about a diameter which is perpendicular to the field. The angular velocity of rotation is 300 revolutions per minute. The area of the coil is 25 cm2 and its resistance is 4.0 Ω. Find (a) the average emf developed in half a turn from a position where the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field, (b) the average emf in a full turn and (c) the net charge displaced in part (a).
A circular copper-ring of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the ring. Consider different pairs of diametrically opposite points on the ring. (a) Between which pair of points is the emf maximum? What is the value of this maximum emf? (b) Between which pair of points is the emf minimum? What is the value of this minimum emf ?
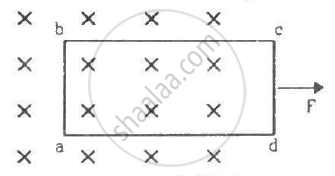
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32 cm × 8.0 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10−5N (see the following figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find (a) this constant speed, (b) the emf induced in the loop, (c) the potential difference between the points aand b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east-west direction and the rear wheel is rotated at an angular speed of 100 revolutions per minute. If the length of each spoke is 30.0 cm and the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 2.0 × 10−5 T, find the emf induced between the axis and the outer end of a spoke. Neglect centripetal force acting on the free electrons of the spoke.
The current in a solenoid of 240 turns, having a length of 12 cm and a radius of 2 cm, changes at a rate of 0.8 A s−1. Find the emf induced in it.
An inductor-coil of inductance 20 mH having resistance 10 Ω is joined to an ideal battery of emf 5.0 V. Find the rate of change of the induced emf at (a) t = 0, (b) t = 10 ms and (c) t = 1.0 s.
A small flat search coil of area 5cm2 with 140 closely wound turns is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet producing magnetic field 0.09T and then quickly removed out of the field region. Calculate:
(a) Change of magnetic flux through the coil, and
(b) emf induced in the coil.
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance ______.
When the rate of change oic current is unity, the induced emf is equal to ______.
The current flowing in a step-down transformer 220 V to 22 V having impedance 220 π is
