Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle is found to be at rest when seen from a frame S1 and moving with constant velocity when seen from another frame S2. Mark out the possible options.
(a) Both the frames are inertial.
(b) Both the frames are non-inertial.
(c) S1 is inertial and S2 is non-inertial.
(d) S1 is non-inertial and S2 is inertial
उत्तर
(a) Both the frames are inertial.
(b) Both the frames are non-inertial.
S1 is moving with constant velocity w.r.t frame S2. So, if S1 is inertial, then S2 will be inertial and if S1 is non-inertial, then S2 will be non-inertial.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the scientist who gave the laws of motion.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Newton’s first law of motion is also called Galileo’s law of ………………………
Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle?
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
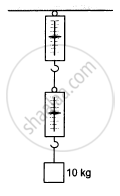
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
'When a hanging carpet is beaten with a stick, the dust particles start coming out of it'. This phenomenon can be best explained by making use of :
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
The amount of inertia of a body depends on its _________.
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of motion
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
Classify the types of force based on their application.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
In a legend, the hero-kid kicked a toy pig so that it is projected with a speed greater than that of its cry. If the weight of the toy pig is assumed to be 5 kg and the time of contact 0.01 sec., the force with which the hero-kid kicked him was ______.
(Speed of cry = 330 m/s)
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| b. Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of the body |
| c. Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| d. Law of conservation of Linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
