Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
उत्तर
A radio can tune to minimum frequency, v1 = 7.5 MHz = 7.5 × 106 Hz
Maximum frequency, v2 = 12 MHz = 12 × 106 Hz
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Corresponding wavelength for v1 can be calculated as:
`lambda_1 = "c"/"v"_1`
= `(3 xx 10^8)/(7.5 xx 10^6)`
= 40 m
Corresponding wavelength for v2 can be calculated as:
`lambda_2 = "c"/"v"_2`
= `(3 xx 10^8)/(12 xx 10^6)`
= 25 m
Thus, the wavelength band of the radio is 40 m to 25 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are infra-red waves often called heat waves? Explain.
What do you understand by the statement, "Electromagnetic waves transport momentum"?
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Give one use of microwaves.
Give one use of ultraviolet radiation.
Name the rays or waves of highest frequency .
Can X-rays be polarised?
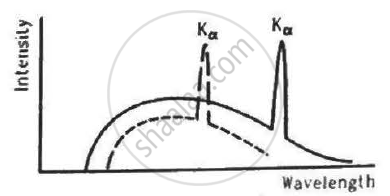
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
X-ray incident on a material
(a) exerts a force on it
(b) transfers energy to it
(c) transfers momentum to it
(d) transfers impulse to it.
Iron emits Kα X-ray of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the times taken by an iron Kα photon to cross through a distance of 3 km.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The Kα X-rays of aluminium (Z = 13) and zinc (Z = 30) have wavelengths 887 pm and 146 pm respectively. Use Moseley's law √v = a(Z − b) to find the wavelengths of the Kα X-ray of iron (Z = 26).
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The distance between the cathode (filament) and the target in an X-ray tube is 1.5 m. If the cutoff wavelength is 30 pm, find the electric field between the cathode and the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Visible light
Name the radiation which can be detected by thermopile.
Answer briefly.
Does an ordinary electric lamp emit EM waves?
Which of the following is a tool used for separating the different color wavelengths from each other?
The half-value thickness of an absorber is defined as the thickness that will reduce exponentially the intensity of a beam of particles by a factor of 2. The half-value thickness in (µm) for lead assuming X-ray beam of wavelength 20 pm, µ = 50 cm-1 for X-rays in lead at wavelength λ = 20 pm, is ______ µm.
What is the speed of radio waves in vacuum?
Name one radiation having the wavelength longer than the wavelength of these radiations.
