Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can X-rays be polarised?
उत्तर
Only transverse waves can be polarised. Since an X-ray is a transverse wave, it can be polarised.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What role dose infra-red radiation play in maintain the Earth’s warmth
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with infrared rays.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
- Name the two waves.
- Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems?
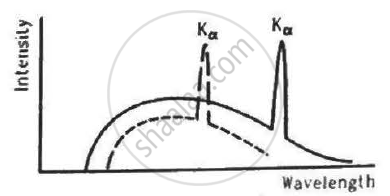
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
X-ray from a Coolidge tube is incident on a thin aluminium foil. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil is found to be I0. The heating current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil will be
(a) zero
(b) < I0
(c) I0
(d) > I0
X-ray incident on a material
(a) exerts a force on it
(b) transfers energy to it
(c) transfers momentum to it
(d) transfers impulse to it.
Consider a photon of continuous X-ray and a photon of characteristic X-ray of the same wavelength. Which of the following is/are different for the two photons?
The X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube has a cutoff wavelength of 80 pm. Find the kinetic energy of the electrons hitting the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
An X-ray tube operates at 40 kV. Suppose the electron converts 70% of its energy into a photon at each collision. Find the lowest there wavelengths emitted from the tube. Neglect the energy imparted to the atom with which the electron collides.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Suppose a monochromatic X-ray beam of wavelength 100 pm is sent through a Young's double slit and the interference pattern is observed on a photographic plate placed 40 cm away from the slit. What should be the separation between the slits so that the successive maxima on the screen are separated by a distance of 0.1 mm?
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Choose the correct option.
How does the frequency of a beam of ultraviolet light change when it travels from air into glass?
Answer briefly.
Why light waves travel in a vacuum whereas sound waves cannot?
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifiers.
- λ3 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
Identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong. Also arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
Identify the electromagnetic wave whose wavelength range is from about 10-12 m to about 10-8 m. Write one use of this.
Identify the electromagnetic wave whose wavelength range is from about 10-3 m to about 10-1 m. Write one use of this.
What is the speed of radio waves in vacuum?
