Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process of expansion and compression as shown in figure 6.1. What will be the value of ∆H for the cycle as a whole?

उत्तर
For a cyclic process, ΔH = 0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Expansion of a gas in vacuum is called free expansion. Calculate the work done and the change in internal energy when 1 litre of ideal gas expands isothermally into vacuum until its total volume is 5 litre?
What will be the work done on an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder, when it is compressed by a constant external pressure, pext in a single step as shown in figure. Explain graphically.
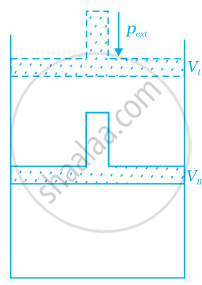
How will you calculate work done on an ideal gas in a compression, when change in pressure is carried out in infinite steps?
Represent the potential energy/enthalpy change in the following processes graphically.
(a) Throwing a stone from the ground to roof.
(b) \[\ce{1/2 H2(g) + 1/2 Cl2 (g) ⇌ HCl (g) Δ_rH^Θ = - 92.32 kJ mol^{-1}}\]
In which of the processes potential energy/enthalpy change is contributing factor to the spontaneity?
Match the following :
| A | B |
| (i) Adiabatic process | (a) Heat |
| (ii) Isolated system | (b) At constant volume |
| (iii) Isothermal change | (c) First law of thermodynamics |
| (iv) Path function | (d) No exchange of energy and matter |
| (v) State function | (e) No transfer of heat |
| (vi) ΔU = q | (f) Constant temperature |
| (vii) Law of conservation of energy | (g) Internal energy |
| (viii) Reversible process | (h) Pext = o |
| (ix) Free expansion | (i) At constant pressure |
| (x) ΔH = q | (j) Infinitely slow process which proceeds through a series of equilibrium states. |
| (xi) Intensive property | (k) Entropy |
| (xii) Extensive property | (l) Pressure |
| (m) Specific heat |
Match the following :
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Entropy of vapourisation | (a) decreases |
| (ii) K for spontaneous process | (b) is always positive |
| (iii) Crystalline solid state | (c) lowest entropy |
| (iv) ∆U in adiabatic expansion of ideal gas | (d) `(∆H_(vap))/T_b` |
Graphically show the total work done in an expansion when the state of an ideal gas is changed reversibly and isothermally from \[\ce{(p_i, V_i)}\] to \[\ce{(p_f , V_f )}\]. With the help of a pV plot compare the work done in the above case with that carried out against a constant external pressure \[\ce{p_f}\].
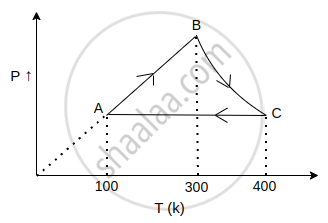
The net work done in the following cycle for one mol of an ideal gas will be ______ (in calorie), where in process BC, PT = constant. (R = 2 cal/mol-K).
1 mole of an ideal monoatomic gas initially at 1 atm and 300 K experiences a process by which pressure is doubled. The nature of the process is unspecified but 6. ΔU = 900 cal. The final volume will be ______ l.
[Given : R = 0.08 atm lit. I mol/K = 2 Cal/K/mol J]
Five moles of an ideal gas at 1 bar and 298 K is expanded into the vacuum to double the volume. The work done is ______.
