Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be ______.
पर्याय
both concave
both convex
the mirror is concave and the lens is convex
the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
उत्तर
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be both concave.
Explanation:
By convention, the focal length of a concave mirror and the focal length of a concave lens are taken as negative. Hence, both the spherical mirror and the thin spherical lens are concave in nature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror?
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Out of convex mirror and concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind the mirror?
With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
In the concave reflector of a torch, the bulb is placed:
(a) between the pole and focus of reflector
(b) at the focus of reflector
(c) between focus and centre of curvature of reflector
(d) at the centre of curvature of reflector
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance.
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
(i) Calculate the image distance.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror?
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
Name the lens which can concentrate sun's rays to a point and burn a hole in a piece of paper.
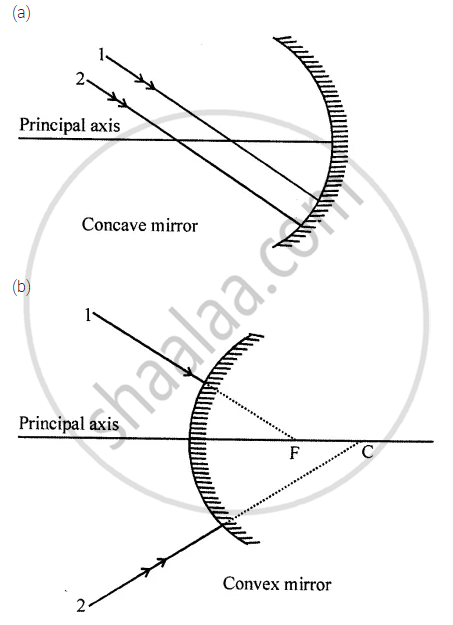
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
The concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted. What effect would this have on the beam of light from the torch?
Between which two points of a concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of -2?
