Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A teacher drew the diagram of the heart on the blackboard and told the students to copy it in their notebooks. Mahesh couldn't see the diagram clearly as it appeared blurred to him.
- Name the defect of the eye Mahesh is suffering from.
- Where is the image formed in this defect?
- Mahesh consults an eye doctor and is prescribed suitable lenses to correct the defect. Which type of lens do his spectacles have?
उत्तर
- Myopia or near-sightedness. Individuals suffering from this illness have difficulty seeing distant objects clearly, resulting in fuzzy vision for faraway objects while keeping crisp focus on close ones.
- The image is formed in front of the retina. This issue arises when the eye's power is excessive, which is typically a result of the crystalline lens's shorter focal length.
- A concave lens. A concave lens, which diverges incoming rays and focuses them on the retina, is widely used to rectify this issue.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
What is the other name for
hypermetropia
What is the far point of a person suffering from myopia (or short-sightedness)?
A person suffering from the eye-defect myopia (short-sightedness) can see clearly only up to a distance of 2 metres. What is the nature and power of lens required to rectify this defect?
The near-point of a person suffering from hypermetropia is at 50 cm from his eye. What is the nature and power of the lens needed to correct this defect? (Assume that the near-point of the normal eye is 25 cm).
What is short-sightedness? State the two causes of short-sightedness (or myopia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect short-sightedness.
(ii) correction of short-sightedness by using a lens.
An eye has a far point of 2 m. What type of lens in spectacles would be needed to increase the far point to infinity? Also calculate the power of lens required. Is this eye long-sighted or short-sighted?
A student cannot see a chart hanging on a wall placed at a distance of 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagrams for the (i) defect of vision and also (ii) for its correction.
An old man cannot see objects closer than 1 m from the eye clearly. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagram for the (i) defect of vision and also (ii) for its correction.
When do we consider a student sitting in the class to be myopic? List two causes of this defect. Explain using a ray diagram how this defect of eye can be corrected.
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
(iii) Give labelled two possible reasons for this eye defect.
(iv) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified.
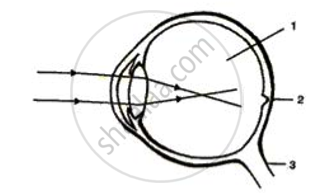
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow :
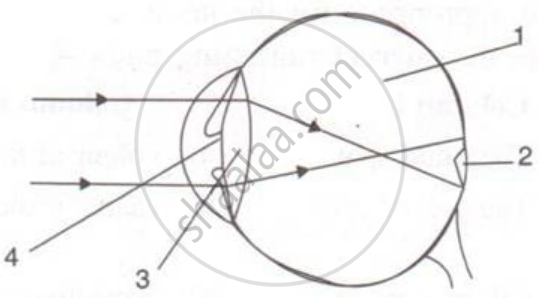
Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
Given below is a diagrammatic representation of a defect of the human eye:
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Mention two reasons for the above defect.
(iii) State how the defect can be rectified.
(iv) Name the part of the eye responsible for maintaining the shape of the eyeball.
Differentiate the eye defects: Myopia and Hypermetropia
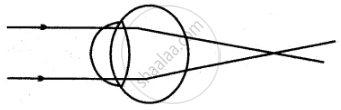
Observe the figure and answer the following questions:
- Name the defect of vision represented in the above figure.
- State the reasons for this defect.
- How is it corrected?
- Draw the diagram to show the correction of this defect.
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
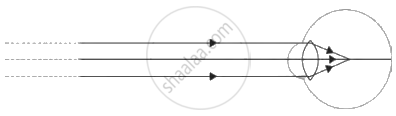
Complete the following table by observing the given figures:
| Figure → | 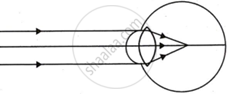 |
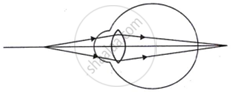 |
| Points ↓ | ||
| (a) Name of the defect | ______ | ______ |
| (b) Position of the image | ______ | ______ |
| (c) Lens used to correct the defect | ______ | ______ |
