Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A transition element X has an electronic configuration [Ar]4s23d3. Predict its likely oxidation states.
उत्तर
Electronic configuration of X = [Ar]4s23d3
Vanadium, a transition element, is the one that has been provided. The variable oxidation states + 2, + 3, + 4 and + 5 will be displayed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why do interstitial compounds have higher melting points than corresponding pure metals?
Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solutions?
Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are trapped inside the crystal lattice of metals. Which of the following is not the characteristic property of interstitial compounds?
When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with \[\ce{HCl}\] it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in excess, reacts with \[\ce{NH3}\] to give an explosive compound (C). Identify compounds A, B and C.
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has highest second ionisation enthalpy?
Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state. How does \[\ce{Fe(III)}\] catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions?
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
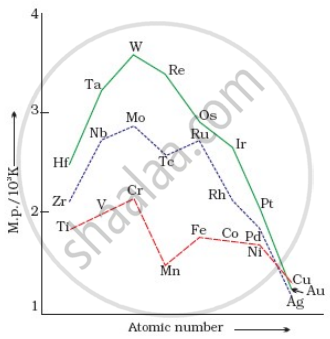
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
Which of the following species has maximum magnetic momentum?
The second ionization enthalpies of chromium and manganese are 1592 and 1509 kJ/mol respectively. Explain the lower value of Mn.
Account for the following:
Zirconium (Zr) and Hafnium (Hf) are difficult to separate.
