Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with \[\ce{HCl}\] it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in excess, reacts with \[\ce{NH3}\] to give an explosive compound (C). Identify compounds A, B and C.
उत्तर
The compounds A, B and C are as follows:
A = \[\ce{MnO2}\], B = \[\ce{Cl2}\], C = \[\ce{NCl3}\]
The reactions are explained as under:
\[\ce{\underset{(A)}{MnO2} + 4HCl -> MnCl2 + \underset{(B)}{Cl2} + 2H2O}\]
\[\ce{\underset{(Excess)}{3Cl2} + NH3 -> \underset{(C)}{NCl3} + 3HCl}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To what extent do the electronic configurations decide the stability of oxidation states in the first series of the transition elements? Illustrate your answer with examples.
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of the non-transition metals? Illustrate with examples.
Give reasons: Sc3+ is colourless in aqueous solution whereas Ti3+ is coloured.
Transition elements form binary compounds with halogens. Which of the following elements will form \[\ce{MF3}\] type compounds?
(i) \[\ce{Cr}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Co}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Cu}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Ni}\]
Match the properties given in Column I with the metals given in Column II.
| Column I (Property) | Column II (Metal) | |
| (i) | An element which can show +8 oxidation state | (a) \[\ce{Mn}\] |
| (ii) | 3d block element that can show | (b) \[\ce{Cr}\] |
| upto +7 oxidation state | (c) \[\ce{Os}\] | |
| (iii) | 3d block element with highest melting point | (d) \[\ce{Fe}\] |
Assertion: \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] iodide is not known.
Reason: \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] oxidises \[\ce{I^-}\] to iodine.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
Passing H2S gas into a mixture of Mn2+ and Ni2+, Cu2+, ions in an acidified aqueous solution precipitates.
On adding NaOH, solution to the aqueous solution of K2CrO7 the colour of the solution changes from
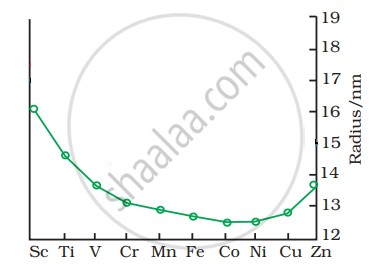
The trend of which property is represented by the following graph?