Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
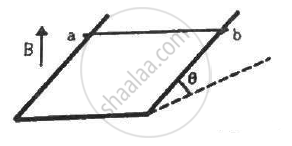
A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth, thick pair of metallic rails joined at the bottom as shown in figure. The plane of the rails makes an angle θ with the horizontal. A vertical magnetic field B exists in the region. If the wire slides on the rails at a constant speed v, show that \[B = \sqrt{\frac{mg R sin\theta}{v l^2 \cos^2 \theta}}\]
उत्तर
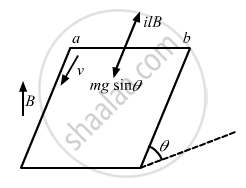
Component of weight along its motion, F' = mgsinθ
The emf induced in the rod due to its motion is given by
e = Bl'v'
Here,
l' = Component of the length of the rod perpendicular to the magnetic field
v' = Component of the velocity of the rod perpendicular to the magnetic field
\[i = \frac{B \times l \times v cos\theta}{R}\]
\[\left| \overrightarrow{F} \right| = i\left| \overrightarrow{l} \times \overrightarrow{B} \right| = ilB\sin(90 - \theta)\]
\[F = ilB = \frac{Blv \cos\theta}{R} \times l \times B\cos\theta\]
\[F = \frac{B^2 l^2 v \cos^2 \theta}{R}\]
The direction of force F is opposite to F.'
Because the rod is moving with a constant velocity, the net force on it is zero.
Thus,
F - F' = 0
F = F'
or
\[\frac{B^2 l^2 v \cos^2 \theta}{R} = mg\sin\theta\]
\[\therefore B = \sqrt{\frac{Rmg\sin\theta}{l^2 v \cos^2 \theta}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the condition under which the charged particles moving with different speeds in the presence of electric and magnetic field vectors can be used to select charged particles of a particular speed.
Depict the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of a diamagnetic material?
A point charge q moving with speed v enters a uniform magnetic field B that is acting into the plane of the paper as shown. What is the path followed by the charge q and in which plane does it move?
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting oscillating electric and magnetic fields of an em wave propagating along + z-direction ?
Show with the help of a diagram how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions?
The motion of copper plate is damped when it is allowed to oscillate between the two poles of a magnet. What is the cause of this damping?
A moving charge produces
Consider a long, straight wire of cross-sectional area A carrying a current i. Let there be n free electrons per unit volume. An observer places himself on a trolley moving in the direction opposite to the current with a speed \[v = \frac{i}{\text{nAe}}\] and separation from the wire by a distance r. The magnetic field seen by the observer is very nearly
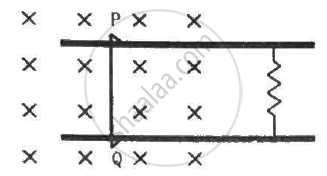
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire PQ has mass m, resistance r and can slide on the smooth, horizontal parallel rails separated by a distance l. The resistance of the rails is negligible. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the rectangular region and a resistance R connects the rails outside the field region. At t = 0, the wire PQ is pushed towards right with a speed v0. Find (a) the current in the loop at an instant when the speed of the wire PQ is v, (b) the acceleration of the wire at this instant, (c) the velocity vas a functions of x and (d) the maximum distance the wire will move.
A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then ______.
-
The presence of a large magnetic flux through a coil maintains a current in the coil if the circuit is continuous.
-
A coil of a metal wire kept stationary in a non– uniform magnetic field has an e.m.f induced in it.
-
A charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic field at an angle of 85° to the magnetic lines of force, the path of the particle is a circle.
-
There is no change in the energy of a charged particle moving in a magnetic field although a magnetic force is acting on it.
A moving charge will gain kinetic energy due to the application of ______.
A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a resultant force ______
A circular coil of radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 3.0 × 10-5 T with its plane perpendicular to the field initially. It is rotated at constant angular speed about an axis along the diameter of coil and perpendicular to magnetic field so that it undergoes half of rotation in 0.2 s. The maximum value of EMF induced (in µV) in the coil will be close to the integer ______.
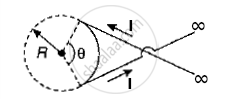
A wire carrying current i has the configuration shown in figure. For the magnetic field to be zero at the centre of the circle, θ must be:
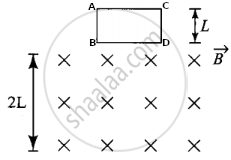
A square coil ABCD with its plane vertical is released from rest in a horizontal uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` of length 2L. The acceleration of the coil is ______.
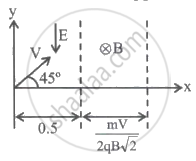
A charged particle of charge q and mass m is projected in a region that contains an electric and magnetic field as shown in the figure with velocity V at an angle of 45° with x-direction. If V = `sqrt((qE)/m)`, then net deviation in particle motion will be (neglect the effect of gravity) in a clockwise direction approx ______ °.