Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
उत्तर
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................................................}\ce{^5CH3}\\
\phantom{..................................................}|\\
\phantom{...................................................}\ce{^4CH2}\\
\phantom{..................................................}|\\
\ce{A + O3 ->[Zn + H2O] H3C - C = O + ^1CH3 - ^2CH2 - ^3C}\\
\phantom{.......................}|\phantom{...........................}||\\
\phantom{.........................}\ce{\underset{Ethanal}{H}}\phantom{....................}\ce{\underset{Pentan - 3 - one}{O}}
\end{array}\]
During ozonolysis, an ozonide having a cyclic structure is formed as an intermediate which undergoes cleavage to give the final products. Ethanal and pentan-3-one are obtained from the intermediate ozonide. Hence, the expected structure of the ozonide is:
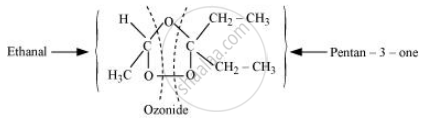
This ozonide is formed as an addition of ozone to ‘A’. The desired structure of ‘A’ can be obtained by the removal of ozone from the ozonide. Hence, the structural formula of ‘A’ is:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H3^1C - ^2CH = ^3C - ^4CH2 - ^5CH3}\\
\phantom{.}|\\\phantom{..........}\ce{CH2 - CH3}\end{array}\]
The IUPAC name of ‘A’ is 3-Ethylpent-2-ene.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write IUPAC name of the product obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compound.
Pent-2-ene
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis products of an alkene? What is the structural formula of the alkene?
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Pentene
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Hexyne
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Toluene
Arrange the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
The addition of HBr to 1-butene gives a mixture of products A, B and C
| (A) | 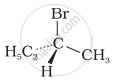 |
| (B) | 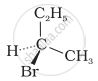 |
| (C) | CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – Br |
The mixture consists of:
Which of the following alkenes on ozonolysis give a mixture of ketones only?
| (i) | CH3 – CH = CH – CH3 |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - C - CH = CH2}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) | 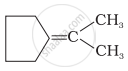 |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...................}\ce{CH3}\\ \phantom{..............}/\\ \ce{(CH3)2 C = C}\\ \phantom{..............}\backslash\\ \phantom{...................}\ce{CH3} \end{array}\] |
In the presence of peroxide addition of HBr to propene takes place according to anti Markovnikov’s rule but peroxide effect is not seen in the case of HCl and HI. Explain.
An alkene 'X' on ozonolysis produces two moles of isovaleraldehyde. Predict the IUPAC name of the alkene.
The major product formed in the following reactions is:
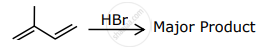
What would be the main product when propene reacts with HBr?
Propene, \[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH2}\] can be converted to 1-propanol by oxidation. Which set of reagents among the following is ideal to effect the conversion ______.
3-Methyl-pent-2-ene on reaction with HBr in presence of peroxide forms an addition product. The number of possible stereoisomers for the product is ______.
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C-C, eight C-H σ bonds and one C-C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write the IUPAC name of ‘A’.
