Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief:
Why is it useful to define the radius of gyration?
उत्तर
Definition: The radius of gyration of a body rotating about an axis is defined as the distance between the axis of rotation and the point at which the entire mass of the body can be concentrated to give the same moment of inertia as that of the body about the given axis.
The moment of inertia (MI) of a body about a given rotation axis depends upon (i) the mass of the body and (ii) the distribution of mass about the axis of rotation. These two factors can be separated by expressing the MI as the product of the mass (M) and the square of a particular distance (k) from the axis of rotation. This distance is called the radius of gyration and is defined as given above. Thus,
I = `sum_"i""m"_"i""r"_"i"^2 = "Mk"^2`
∴ k = `sqrt("I"/"M")`
The pressure applied at a specific location can be determined with the use of the radius of gyration. When calculating the strength and intensity between specified cross-sections of a region, it is highly helpful. The radius of gyration for a given point decreases with increasing distance from the rotational axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define radius of gyration
Discuss the necessity of radius of gyration.
A cyclist riding a bicycle at a speed of `14sqrt3` m/s takes a turn around a circular road of radius `20sqrt3` m without skidding. Given g = 9.8 m/s2, what is his inclination to the vertical ______.
Find the radius of gyration of a uniform disc about an axis perpendicular to its plane and passing through its center.
The ratio of radii of gyration of a ring to a disc (both circular) of same radii and mass, about a tangential axis perpendicular to the plane is
The radius of the earth and the radius of orbit around the sun are 6371 km and 149 x 106 km respectively. The order of magnitude of the diameter of the orbit is greater than that of earth by ______.
The radius of gyration of a uniform rod of length `l`, about an axis passing through a point `l/4` away from the centre of the rod, and perpendicular to it, is: ____________.
Four particles each of mass 'M' are placed at corners of a square of side 'L'. The radius of gyration of the system about an axis perpendicular to the square and passing through its centre is ______.
A fly wheel is accelerated uniformly from rest and rotates through 5 rad in the first second. The angle rotated by the fly wheel in the next second, will be ______.
A circular disc of radius R is removed from a bigger circular disc of radius 2R such that the circumferences of the discs coincide. The centre of mass of the new disc is α/R form the centre of the bigger disc. The value of α is ______.
Let M be the mass and L be the length of a thin uniform rod. In first case, axis of rotation is passing through centre and perpendicular to the length of the rod. In second case, axis of rotation is passing through one end and perpendicular to the length of the rod. The ratio of radius of gyration in first case to second case is ______.
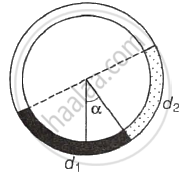
There is a circular tube in a vertical plane. Two liquids which do not mix and of densities d1 and d2 are filled in the tube. Each liquid subtends 90° angle at centre. Radius joining their interface makes an angle α with vertical. Ratio d1/d2 is ______.
The ratio of the radii of gyration of a circular disc and a circular ring of the same radius about a tangential axis in the plane is ______.
Given the nuclear radius of 16O is 3.024 fm, find that of 235U.
What is the radius of gyration of a right circular cone of base radius R for rotation about the central symmetry axis of the cone?
Define radius of gyration
On what factors does radius of gyration depend?
On what factors radius of gyration does not depend?
Define the Necessity radius of gyration.
