Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question in detail.
State Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion.
उत्तर
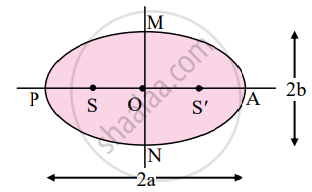
1. Kepler’s law of orbits:
Statement:
All planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun with the Sun at one of the foci of the ellipse.
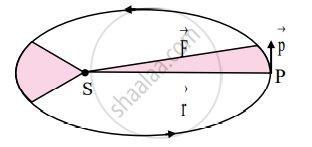
2. Kepler’s law of equal areas:
Statement:
The line that joins a planet and the Sun sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
3. Kepler’s law of periods:
Statement:
The square of the time period of revolution of a planet around the Sun is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of the ellipse traced by the planet.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Kepler's law of orbit and law of equal areas.
Let us assume that our galaxy consists of 2.5 × 1011 stars each of one solar mass. How long will a star at a distance of 50,000 ly from the galactic centre take to complete one revolution? Take the diameter of the Milky Way to be 105 ly
State Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
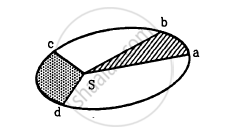
In the Following figure shows the elliptical path of a planet about the sun. The two shaded parts have equal area. If t1 and t2 be the time taken by the planet to go from a to b and from c to d respectively,
Answer the following question.
State Kepler’s law of equal areas.
Answer the following question.
State Kepler’s law of the period.
The orbit of a planet revolving around a star is _______.
The square of its period of revolution around the sun is directly proportional to the _______ of the mean distance of a planet from the sun.
Observe the given figure and answer these following questions.

The orbit of a planet moving around the Sun
- What is the conclusion about the orbit of a planet?
- What is the relation between velocity of planet and distance from sun?
- Explain the relation between areas ASB, CSD and ESF.
Write the Kepler's laws.
The mass and radius of earth is 'Me' and 'Re' respectively and that of moon is 'Mm' and 'Rm' respectively. The distance between the centre of the earth and that of moon is 'D'. The minimum speed required for a body (mass 'm') to project from a point midway between their centres to escape to infinity is ______.
The earth moves around the sun in an elliptical orbit as shown in the figure. The ratio, `"OA"/"OB"` = x. The ratio of the speed of the earth at Band at A is ______.

To verify Kepler's third law graphically four students plotted graphs. Student A plotted a graph of T (period of revolution of planets) versus r (average distance of planets from the sun) and found the plot is straight line with slope 1.85. Student B plotted a graph of T2 v/s r3 and found the plot is straight line with slope 1.39 and negative Y-intercept. Student C plotted graph of log T v/s log r and found the plot is straight line with slope 1.5. Student D plotted graph of log T v/s log r and found the plot is straight line with slope 0.67 and with negative X-intercept. The correct graph is of student
A planet revolves in an elliptical orbit around the sun. The semi-major and minor axes are a and b, then the time period is given by:
In our solar system, the inter-planetary region has chunks of matter (much smaller in size compared to planets) called asteroids. They ______.
If the sun and the planets carried huge amounts of opposite charges ______.
- all three of Kepler’s laws would still be valid.
- only the third law will be valid.
- the second law will not change.
- the first law will still be valid.
If the sun and the planets carried huge amounts of opposite charges ______.
- all three of Kepler’s laws would still be valid.
- only the third law will be valid.
- the second law will not change.
- the first law will still be valid.
Supposing Newton’s law of gravitation for gravitation forces F1 and F2 between two masses m1 and m2 at positions r1 and r2 read F1 = – F2 = `- r_12/r_12^3 GM_0^2 ((m_1m_2)/M_0^2)^n` where M0 is a constant of dimension of mass r12 = r1 – r2 and n is a number. in such a case.
- the acceleration due to gravity on earth will be different for different objects.
- none of the three laws of Kepler will be valid.
- only the third law will become invalid.
- for n negative, an object lighter than water will sink in water.
Give one example each of central force and non-central force.
Draw areal velocity versus time graph for mars.
What is the direction of areal velocity of the earth around the sun?
Out of aphelion and perihelion, where is the speed of the earth more and why?
Earth’s orbit is an ellipse with eccentricity 0.0167. Thus, earth’s distance from the sun and speed as it moves around the sun varies from day to day. This means that the length of the solar day is not constant through the year. Assume that earth’s spin axis is normal to its orbital plane and find out the length of the shortest and the longest day. A day should be taken from noon to noon. Does this explain variation of length of the day during the year?
A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit has:
- a constant velocity of revolution.
- has the least velocity when it is nearest to the sun.
- its areal velocity is directly proportional to its velocity.
- areal velocity is inversely proportional to its velocity.
- to follow a trajectory such that the areal velocity is constant.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
lf the angular momentum of a planet of mass m, moving around the Sun in a circular orbit is L, about the center of the Sun, and its areal velocity is ______.
Halley's Comet revolves around the sun for a time period of 76 years. The aphelion distance if perihelion is given by 8.9 × 1010 m, will be ______.
(Take, the mass of sun = 2 × 1030 kg and G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm3/kg2)
