Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly explain how the output voltage/current is unidirectional.
उत्तर
The ac to be transformed is connected across the primary (P1P2) of a transformer. In the first half of the cycle, suppose P1 is positive and P2 is negative. This makes S1 of the secondary coil positive and S2 negative. As a result, the diode D1 will be forward biased, and hence, it will conduct. The current flows through D1 and from X to Y through RL and we get an output. In this cycle, the diode D2 does not conduct as it is reverse biased. Similarly, in the second half of the cycle, D1 does not conduct but D2 conducts. However, the current flows from X to Y again. Hence, in the entire process, the current flows in one direction itself.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In half-wave rectification, what is the output frequency if the input frequency is 50 Hz. What is the output frequency of a full-wave rectifier for the same input frequency.
When the diode shows saturated current, dynamic place resistance is _____________ .
Fill in the blank.
The ability of a junction diode to __________ an alternating voltage is based on the fact that it allows current to pass only when it is forward biased.
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier.
The output of the given circuit in figure is given below.
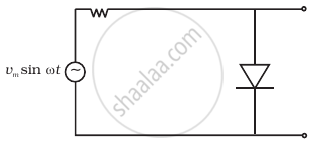
With the help of a circuit diagram, explain briefly how a p-n junction diode works as a half-wave rectifier.
Give two differences between a half-wave rectifier and a full-wave rectifier.
With the help of a circuit diagram, explain how a full wave rectifier gives output rectified voltage corresponding to both halves of the input ac voltage.
Name the device which utilizes the unilateral action of a pn diode to convert ac into dc.
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show graphically how the output voltage varies with time.
