Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly explain ‘rolling friction.'
उत्तर
The invention of the wheel plays a crucial role in human civilization. One of the important applications is suitcases with rolling on coasters. Rolling wheels makes it easier than carrying luggage. When an object moves on a surface, essentially it is sliding on it. But wheels move on the surface through rolling motion. In rolling motion when a wheel moves on a surface, the point of contact with the surface is always at rest. Since Rolling and kinetic friction, the point of contact is at rest, there is no relative motion between the wheel and surface.
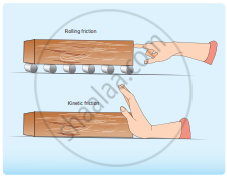
Rolling and kinetic friction
Hence the frictional force is very less. At the same time, if an object moves without a wheel, there is a relative motion between the object and the surface. As a result, the frictional force is larger. This makes it difficult to move the object. The figure shows the difference between rolling and kinetic friction. Ideally in pure rolling, the motion of the point of contact with the surface should be at rest, but in practice, it is not so.
Due to the elastic nature of the surface at the point of contact, there will be some deformation on the object at this point on the wheel or surface as shown in the figure. Due to this deformation, there will be minimal friction between wheel and surface. It is called ‘rolling friction. In fact, rolling friction is much smaller than kinetic friction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of mass m begins to move on the plane inclined at an angle θ. The coefficient of static friction of inclined surfaces is µs. The maximum static friction experienced by the mass is ______
Explain various types of friction.
Suggest a few methods to reduce friction.
Briefly explain the origin of friction. Show that in an inclined plane, the angle of friction is equal to the angle of repose.
A uniform chain of length 3 metres and mass 3 kg overhangs a smooth table with 2 metres laying on the table. If k is the kinetic energy of the chain in joule as it completely slips off the table, then the value of k is ______.
(Take g = 10 m/s2)
A 40 kg wooden crate is being pushed across a wooden floor with a force of 160 N. If µk = 0.3, the acceleration of the crate is ______ m/s2. (g = 10 m/s2}
A block of mass m = 1 kg moving on horizontal surface with speed u = 2 m/s enters a rough horizontal patch ranging from x = 0.10 m to x = 2.00 m. If the retarding force fr on the block in this range is inversely proportional to x over this range i.e.
fr = `"-k"/x` 0.10 < x < 2.00
= 0 for x < 0.10 and x > 2.00
If k = 0.5 J then the speed of this block as it crosses the patch is (use ℓn 20 = 3)
The minimum radius of a circle along which a cyclist can ride with a velocity 18 km/hr if the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road is µ = 0.5, is ______ (Take g = 10 m/s2)
Block A has a mass of 2 kg and block B has 20 kg. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the horizontal surface is 0.1, and B is accelerating towards the right with a = 2 m/s2, then the mass of the block C will be ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)

A body starts from rest on a long inclined plane of slope 45°. The coefficient of friction between the body and the plane varies as µ = 0.3 x, where x is distance travelled down the plane. The body will have maximum speed (for g = 10 m/s2) when x = ______.
