Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Briefly explain ‘rolling friction.'
Solution
The invention of the wheel plays a crucial role in human civilization. One of the important applications is suitcases with rolling on coasters. Rolling wheels makes it easier than carrying luggage. When an object moves on a surface, essentially it is sliding on it. But wheels move on the surface through rolling motion. In rolling motion when a wheel moves on a surface, the point of contact with the surface is always at rest. Since Rolling and kinetic friction, the point of contact is at rest, there is no relative motion between the wheel and surface.
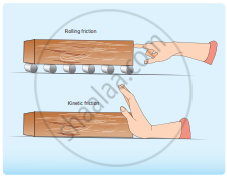
Rolling and kinetic friction
Hence the frictional force is very less. At the same time, if an object moves without a wheel, there is a relative motion between the object and the surface. As a result, the frictional force is larger. This makes it difficult to move the object. The figure shows the difference between rolling and kinetic friction. Ideally in pure rolling, the motion of the point of contact with the surface should be at rest, but in practice, it is not so.
Due to the elastic nature of the surface at the point of contact, there will be some deformation on the object at this point on the wheel or surface as shown in the figure. Due to this deformation, there will be minimal friction between wheel and surface. It is called ‘rolling friction. In fact, rolling friction is much smaller than kinetic friction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain various types of friction.
A heavy uniform chain lies on a horizontal table. If the coefficient of friction between the chain and the table is 0.25, then the maximum fraction of the length of the chain that can hang over one edge of the table is
A uniform metal chain is placed on a rough table such that one end of the chain hangs down over the edge of the table. When two-thirds of its chain length hangs over the edge the chain start sliding. Then the coefficient of static friction is:
A block of mass 20 kg is sliding on a surface is inclined at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. What will be the acceleration of the block if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.7?
If a body of mass m is moving on a rough horizontal surface of coefficient of kinetic friction µ, the net resultant force exerted by surface on the body is ______.
A block of mass m is pulled by a constant power P placed on a rough horizontal plane. The friction co-efficient between the block and the surface is µ. Maximum velocity of the block will be:
A block of mass m = 1 kg moving on horizontal surface with speed u = 2 m/s enters a rough horizontal patch ranging from x = 0.10 m to x = 2.00 m. If the retarding force fr on the block in this range is inversely proportional to x over this range i.e.
fr = `"-k"/x` 0.10 < x < 2.00
= 0 for x < 0.10 and x > 2.00
If k = 0.5 J then the speed of this block as it crosses the patch is (use ℓn 20 = 3)
The minimum radius of a circle along which a cyclist can ride with a velocity 18 km/hr if the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road is µ = 0.5, is ______ (Take g = 10 m/s2)
Block A has a mass of 2 kg and block B has 20 kg. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the horizontal surface is 0.1, and B is accelerating towards the right with a = 2 m/s2, then the mass of the block C will be ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)

The coefficient of static friction between a car's tires and a level road is 0.80. If the car is to be stopped in a maximum time of 3.0 s, its speed cannot exceed.
