Advertisements
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 3 - Laws of motion Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 3 - Laws of motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Laws of motion
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 3 Laws of motion Evaluation [Pages 160 - 165]
Multiple Choice Questions
When a car takes a sudden left turn in the curved road, passengers are pushed towards the right due to ______
inertia of direction
inertia of motion
inertia of rest
absence of inertia
An object of mass m held against a vertical wall by applying horizontal force F as shown in the figure. The minimum value of the force F is ______

Less than mg
Equal to mg
Greater than mg
Cannot determine
A vehicle is moving along the positive x-direction, if a sudden brake is applied, then ______
the frictional force acting on the vehicle is along negative x-direction
the frictional force acting on the vehicle is along the positive x-direction
no frictional force acts on the vehicle
the frictional force acts in a downward direction
A book is at rest on the table which exerts a normal force on the book. If this force is considered a reaction force, what is the action force according to Newton’s third law?
The gravitational force exerted by Earth on the book
The gravitational force exerted by the book on Earth
Normal force exerted by the book on the table
None of the above
Two masses m1 and m2 are experiencing the same force where m1 < m2. The ratio of their acceleration `a_1/a_2` is ______
1
less than 1
greater than 1
all the three cases
Choose an appropriate free body diagram for the particle experiencing net acceleration along the negative y-direction. (Each arrow mark represents the force acting on the system).
A particle of mass m sliding on the smooth double inclined plane (shown in the figure) will experience ______

greater acceleration along the path AB
greater acceleration along the path AC
same acceleration in both the paths
no acceleration in both the paths
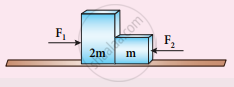
Two blocks of masses m and 2m are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown. In the first case, only a force F1 is applied from the left. Later only a force F2 is applied from the right. If the force acting at the interface of the two blocks in the two cases is the same, then F1 : F2 is ______
1:1
1:2
2:1
1:3
Force acting on the particle moving with constant speed is ______
always zero
need not be zero
always non zero
cannot be concluded
An object of mass m begins to move on the plane inclined at an angle θ. The coefficient of static friction of inclined surfaces is µs. The maximum static friction experienced by the mass is ______
mg
µsmg
µsmg sinθ
µs mg cosθ
When the object is moving at a constant velocity on the rough surface, ______
the net force on the object is zero
no force acts on the object
the only external force acts on the object
only kinetic friction acts on the object
When an object is at rest on the inclined rough surface, ______
static and kinetic frictions acting on the object is zero
static friction is zero but kinetic friction is not zero
static friction is not zero and kinetic friction is zero
static and kinetic frictions are not zero
The centrifugal force appears to exist ______
only in inertial frames
only in rotating frames
in any accelerated frame
both in inertial and non-inertial frames
Choose the correct statement from the following.
Centrifugal and centripetal forces are action-reaction pairs
Centripetal forces is a natural force
Centrifugal force arises from gravitational force
The centripetal force acts towards the centre and centrifugal force appears to act away from the centre in a circular motion
If a person moving from pole to equator, the centrifugal force acting on him ______
increases
decreases
remains the same
increases and then decreases
Short Answer Questions
Explain the concept of inertia. Write two examples each for the inertia of motion, the inertia of rest, and inertia of direction.
State Newton’s second law.
Define one newton.
Show that impulse is the change of momentum.
Using a free body diagram, show that it is easy to pull an object than to push it.
Explain various types of friction.
Suggest a few methods to reduce friction.
What is the meaning of ‘pseudo force’?
State the empirical laws of static and kinetic friction.
State Newton’s third law.
What are inertial frames?
Under what condition will a car skid on a leveled circular road?
Long Answer Questions
Prove the law of conservation of linear momentum. Use it to find the recoil velocity of a gun when a bullet is fired from it.
What are concurrent forces?
State Lami’s theorem.
Explain the motion of blocks connected by a string in (i) Vertical motion (ii) Horizontal motion.
Briefly explain the origin of friction. Show that in an inclined plane, the angle of friction is equal to the angle of repose.
State Newton’s three laws and discuss their significance.
Explain the similarities and differences of centripetal and centrifugal forces.
Briefly explain ‘centrifugal force’ with suitable examples.
Briefly explain ‘rolling friction.'
Explain the need for banking of tracks.
Calculate the centripetal acceleration of the Moon towards the Earth.
Numerical Problems
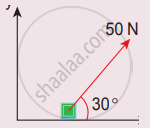
A force of 50N acts on the object of mass of 20 kg. shown in the figure. Calculate the acceleration of the object in x and y directions.
A spider of mass 50 g is hanging on a string of a cobweb as shown in the figure. What is the tension in the string?

What is the reading shown in spring balance?

The physics books are stacked on each other in the sequence: +1 volumes 1 and 2; +2 volumes 1 and 2 on a table.
a) Identify the forces acting on each book and draw the free body diagram.
b) Identify the forces exerted by each book on the other.
A bob attached to the string oscillates back and forth. Resolve the forces acting on the bob into components. What is the acceleration experienced by the bob at an angle θ?
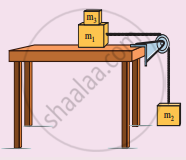
Two masses m1 and m2 are connected with a string passing over a frictionless pulley fixed at the comer of the table as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction of mass m1 with the table is µs Calculate the minimum mass m3 that may be placed on m1 to prevent it from sliding. Check if m1 = 15 kg, m2 = 10 kg, m3 = 25 and µs = 0.2.
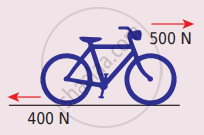
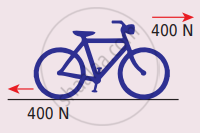
Calculate the acceleration of the bicycle of mass 25 kg as shown in Figures 1 and 2.
Apply Lami’s theorem on the slingshot and calculate the tension in each string?

A football player kicks a 0.8 kg ball and imparts it a velocity of 12 ms-1. The contact between the foot and ball is only for one-sixtieth of a second. Find the average kicking force.
A stone of mass 2 kg is attached to a string of length 1 meter. The string can withstand a maximum tension of 200 N. What is the maximum speed that stone can have during the whirling motion?
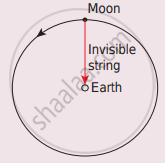
Imagine that the gravitational force between Earth and Moon is provided by an invisible string that exists between the Moon and Earth. What is the tension that exists in this invisible string due to Earth’s centripetal force? (Mass of the Moon = 7.34 × 1022 kg, Distance between Moon and Earth = 3.84 × 108 m)
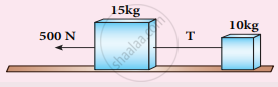
Two bodies of masses 15 kg and 10 kg are connected with light string kept on a smooth surface. A horizontal force F=500 N is applied to a 15 kg as shown in the figure. Calculate the tension acting in the string?
People often say “For every action, there is an equivalent opposite reaction”. Here they meant ‘action of a human’. Is it correct to apply Newton’s third law to human actions? What is mean by ‘action’ in Newton's third law? Give your arguments based on Newton’s laws.
A car takes a turn with a velocity of 50 ms-1 on the circular road of a radius of curvature of 10 m. calculate the centrifugal force experienced by a person of mass 60 kg inside the car?
A long stick rests on the surface. A person standing 10 m away from the stick. With what minimum speed an object of mass 0.5 kg should he has thrown so that it hits the stick. (Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.7).
Solutions for 3: Laws of motion
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 3 - Laws of motion Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 3 - Laws of motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 3 - Laws of motion
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 3 (Laws of motion) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 3 Laws of motion are Introduction to Laws of Motion, Newton's Law, Application of Newton's Law, LAMI's Theorem, Law of Conservation of Total Linear Momentum, Friction, Dynamic of Circular Motion.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Laws of motion exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Laws of motion Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.