Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 8 - Heat and Thermodynamics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 8 - Heat and Thermodynamics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Heat and Thermodynamics
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 8 Heat and Thermodynamics Evaluation [Pages 156 - 162]
Multiple choice questions
In hot summer after a bath, the body’s __________.
internal energy decreases
internal energy increases
heat decreases
no change in internal energy and heat
The graph between volume and temperature in Charles’ law is _________.
an ellipse
a circle
a straight line
a parabola
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
isothermal
adiabatic
isobaric
isochoric
An ideal gas passes from one equilibrium state (P1, V1, T1, N) to another equilibrium state (2P1, 3V1, T2, N). Then
T1 = T2
T1 = `"T"_2/6`
T1 = 6T2
T1 = 3T2
When a uniform rod is heated, which of the following quantity of the rod will increase
mass
weight
center of mass
moment of inertia
When food is cooked in a vessel by keeping the lid closed, after some time the steam pushes the lid outward. By considering the steam as a thermodynamic system, then in the cooking process
Q > 0, W > 0
Q < 0, W > 0
Q > 0, W < 0
Q < 0, W < 0
When you exercise in the morning, by considering your body as a thermodynamic system, which of the following is true?
ΔU > 0, W > 0
ΔU < 0, W > 0
ΔU < 0, W < 0
ΔU = 0, W > 0
A hot cup of coffee is kept on the table. After some time it attains a thermal equilibrium with the surroundings. By considering the air molecules in the room as a thermodynamic system, which of the following is true
ΔU > 0, Q = 0
ΔU > 0, W < 0
ΔU > 0, Q > 0
ΔU = 0, Q > 0
An ideal gas is taken from (Pi, Vi) to (Pf, Vf) in three different ways. Identify the process in which the work done on the gas the most.

Process A
Process B
Process C
Equal work is done in Process A, B and C
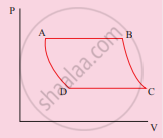
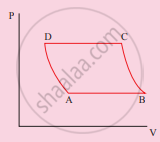
The V-T diagram of an ideal gas which goes through a reversible cycle A→B→C→D is shown below. (Processes D→A and B→C are adiabatic)
The corresponding PV diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic)
A distant star emits radiation with maximum intensity at 350 nm. The temperature of the star is ____________.
8280 K
5000 K
7260 K
9044 K
Identify the state variables given here?
Q, T, W
P, T, U
Q, W
P, T, Q
In an isochoric process, we have ____________.
W = 0
Q = 0
∆U = 0
∆T = 0
The efficiency of a heat engine working between the freezing point and boiling point of water is ____________.
6.25%
20%
26.8%
12.5%
An ideal refrigerator has a freezer at a temperature of −12°C. The coefficient of performance of the engine is 5. The temperature of the air (to which the heat ejected) is ____________.
50°C
45.2°C
40.2°C
37.5°C
Short answer questions
‘An object contains more heat’- is it a right statement? If not why?
Obtain an ideal gas law from Boyle’s and Charles’ law.
Define one mole.
Define specific heat capacity.
Write the unit of specific heat capacity.
Define molar specific heat capacity.
What is a thermal expansion?
Give the expression for linear thermal expansion.
Give the expression for area thermal expansion.
Give the expression for volume thermal expansion.
Define latent heat capacity.
Write the unit of latent heat capacity.
State Stefan-Boltzmann law.
What is Wien’s law?
Define thermal conductivity.
Write the unit of thermal conductivity.
What is a black body?
What is a thermodynamic system? Give examples.
What are the different types of thermodynamic systems?
What is meant by ‘thermal equilibrium’?
What is mean by state variable? Give example.
What are intensive and extensive variables? Give examples.
State zeroth law of thermodynamics.
Define the internal energy of the system.
Are internal energy and heat energy the same? Explain.
Define one calorie.
Did joule converted mechanical energy to heat energy? Explain.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
Can we measure the temperature of the object by touching it?
Give the sign convention for Q and W.
Define the quasi-static process.
Give the expression for work done by the gas.
What is a PV diagram?
Explain why the specific heat capacity at constant pressure is greater than the specific heat capacity at constant volume.
Give the equation of state for an isothermal process.
Give an expression for work done in an isothermal process.
Express the change in internal energy in terms of molar specific heat capacity.
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an adiabatic process.
Apply first law for an isobaric process.
Give the equation of state for an adiabatic process.
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
If the piston of a container is pushed fast inward. Will the ideal gas equation be valid in the intermediate stage? If not, why?
Draw the PV diagram for the isothermal process.
Draw the PV diagram for the adiabatic process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isobaric process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isochoric process.
What is a cyclic process?
What is meant by a reversible and irreversible processes?
State Clausius form of the second law of thermodynamics.
State Kelvin-Planck's statement of the second law of thermodynamics.
Define heat engine.
What are the processes involves in a Carnot engine?
Can the given heat energy be completely converted to work in a cyclic process? If not, when can the heat can completely converted to work?
State the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy.
Why does heat flow from a hot object to a cold object?
Define the coefficient of performance.
Long answer Questions
Explain the meaning of heat and work with suitable examples.
Discuss the ideal gas laws.
Explain in detail the thermal expansion.
Describe the anomalous expansion of water. How is it helpful in our lives?
Explain Calorimetry and derive an expression for final temperature when two thermodynamic systems are mixed.
Discuss various modes of heat transfer.
Explain in detail Newton’s law of cooling.
Explain Wien’s law and why our eyes are sensitive only to visible rays?
Discuss the thermal equilibrium.
Discuss the mechanical equilibrium.
Discuss the chemical equilibrium.
Discuss the thermodynamic equilibrium.
Explain Joule’s Experiment of the mechanical equivalent of heat.
Derive the expression for the work done in a volume change in a thermodynamic system.
Derive Meyer’s relation for an ideal gas.
Explain in detail the isothermal process.
Derive the work done in an isothermal process.
Explain in detail an adiabatic process.
Derive the work done in an adiabatic process.
Explain the isobaric process and derive the work done in this process.
Explain in detail the isochoric process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
Explain the heat engine and obtain its efficiency.
Explain in detail the Carnot heat engine.
Derive the expression for Carnot engine efficiency.
Explain the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy.
Explain in detail the working of a refrigerator.
Numerical Problems
Calculate the number of moles of air is in the inflated balloon at room temperature as shown in the figure.

The radius of the balloon is 10 cm, and the pressure inside the balloon is 180 kPa.
In the planet Mars, the average temperature is around −53°C and atmospheric pressure is 0.9 kPa. Calculate the number of moles of the molecules in unit volume in the planet Mars? Is this greater than that in earth?
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gases, calculate the final equilibrium temperature of the container.
The temperature of a uniform rod of length L having a coefficient of linear expansion αL is changed by ∆T. Calculate the new moment of inertia of the uniform rod about the axis passing through its center and perpendicular to an axis of the rod.
Draw the TP diagram (P-x axis, T-y axis), VT(T-x axis, V-y axis) diagram for
- Isochoric process
- Isothermal process
- Isobaric process
A man starts bicycling in the morning at a temperature around 25°C, he checked the pressure of tire which is equal to be 500 kPa. Afternoon he found that the absolute pressure in the tyre is increased to 520 kPa. By assuming the expansion of tyre is negligible, what is the temperature of tyre at afternoon?
Normal human body of the temperature is 98.6°F. During high fever, if the temperature increases to 104°F, what is the change in peak wavelength that emitted by our body? (Assume human body is a black body)
In an adiabatic expansion of the air, the volume is increased by 4%, what is the percentage change in pressure? (For air γ = 1.4)
In a petrol engine, (internal combustion engine) air at atmospheric pressure and temperature of 20°C is compressed in the cylinder by the piston to `1/8` of its original volume. Calculate the temperature of the compressed air. (For air γ = 1.4)
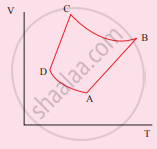
Consider the following cyclic process consist of isotherm, isochoric and isobar which is given in the figure.
Draw the same cyclic process qualitatively in the V-T diagram where T is taken along the x-direction and V is taken along the y-direction. Analyze the nature of heat exchange in each process.
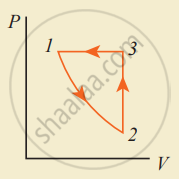
An ideal gas is taken in a cyclic process as shown in the figure. Calculate
- work done by the gas
- work done on the gas
- Net work done in the process

For a given ideal gas 6 × 105 J heat energy is supplied and the volume of gas is increased from 4 m3 to 6 m3 at atmospheric pressure. Calculate
- the work done by the gas
- change in internal energy of the gas
- graph this process in PV and TV diagram
Suppose a person wants to increase the efficiency of the reversible heat engine that is operating between 100°C and 300°C. He had two ways to increase efficiency.
- By decreasing the cold reservoir temperature from 100°C to 50°C and keeping the hot reservoir temperature constant
- by increasing the temperature of the hot reservoir from 300°C to 350°C by keeping the cold reservoir temperature constant.
Which is the suitable method?
A Carnot engine whose efficiency is 45% takes heat from a source maintained at a temperature of 327°C. To have an engine of efficiency of 60% what must be the intake temperature for the same exhaust (sink) temperature?
An ideal refrigerator keeps its content at 0°C while the room temperature is 27°C. Calculate its coefficient of performance.
Solutions for 8: Heat and Thermodynamics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 8 - Heat and Thermodynamics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 8 - Heat and Thermodynamics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 8 - Heat and Thermodynamics
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 8 (Heat and Thermodynamics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 8 Heat and Thermodynamics are Specific Heat Capacity, Introduction to Thermal Properties of Matter, Law of Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics, Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, Internal Energy (U), Thermodynamic Process, Heat Engine, Refrigerator, Heat and Temperature.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Heat and Thermodynamics exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Heat and Thermodynamics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.