Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Derive the expression for the work done in a volume change in a thermodynamic system.
Solution
Work done in volume changes: Consider a gas contained in the cylinder fitted with a movable piston. Suppose the gas is expanded quasi-statically by pushing the piston by a small distance dx. Since the expansion occurs quasi-statically the pressure, temperature and internal energy will have unique values at every instant.
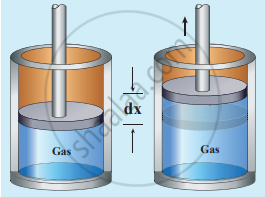
Work done by the gas
The small work done by the gas on the piston
dW = Fdx ….........(1)
The force exerted by the gas on the piston F = PA.
Here A is the area of the piston and P is the pressure exerted by the gas on the piston.
Equation (1) can be rewritten as Work done by the gas
dW = PA dx …..........(2)
But Adx = dV= change in volume during this expansion process.
So the small work done by the gas during the expansion is given by
dW = PdV .........….(3)
dV is positive since the volume is increased. Here, dW is positive.
In general, the work done by the gas by increasing the volume from Vi to Vf is given by
W = `int_("V"_"i")^("V"_"f") "PdV"` ..........(4)
Suppose if the work is done on the system, then Vi > Vf. Then, W is negative.
Note here the pressure P is inside the integral in equation (4). It implies that while the system is doing work, the pressure need not be constant. To evaluate the integration we need to first express the pressure as a function of volume and temperature using the equation of state.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The change in internal energy in a reaction when 2kJ of heat is released by the system and 6 kJ of work is done on the system will be ______.
Are internal energy and heat energy the same? Explain.
Define one calorie.
Did joule converted mechanical energy to heat energy? Explain.
Define the quasi-static process.
Give the expression for work done by the gas.
An ideal gas is allowed to expand in a well insulated container against a constant external pressure of 2.5 bar from an initial volume of 2.50 dm3 to a final volume of 4.50 dm3. The change in internal energy (∆U) of the gas will be ______.
When a system absorbs 8 kJ of heat and does 2.2 kJ of work on surrounding, calculate the internal energy change.
An ideal gas expands against a constant external pressure of 2.0 atmosphere from 20 litre to 40 litre and absorbs 10 kJ of heat from the surrounding. What is the change in the internal energy of the system?
(Given: 1 atm-litre = 101.3 J)
The value of Δ U is ______ when 2 kJ of heat is released and 6 kJ of work is done on the system.
