Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 2 - Kinematics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 2 - Kinematics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Kinematics
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 2 Kinematics Evaluation [Pages 98 - 102]
Multiple Choice Questions
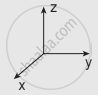
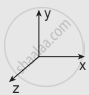
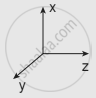
Which one of the following Cartesian coordinate systems are not followed in physics?
Identify the unit vector in the following.
`hati + hatj`
`hati/sqrt2`
`hatk - hatj/sqrt2`
`(hati + hatj)/sqrt2`
Which one of the following physical quantities cannot be represented by a scalar?
Mass
length
momentum
magnitude of acceleration
Two objects of masses m1 and m2 fall from the heights h1 and h2 respectively. The ratio of the magnitude of their momenta when they hit the ground is ______
`sqrt(h_1/h_2)`
`sqrt((m_1h_1)/(m_2h_2))`
`m_1/m_2sqrt(h_1/h_2)`
`m_1/m_2`
If a particle has negative velocity and negative acceleration, its speed ______
increases
decreases
remains same
zero
If the velocity is `vecv = 2hati + t^2hatj - 9veck`, then the magnitude of acceleration at t = 0.5 s is ______
1m s-2
2 m s-2
zero
-1 m s-2
If an object is dropped from the top of a building and it reaches the ground at t = 4 s, then the height of the building is ______
(ignoring air resistance) (g = 9.8 ms–2)
77.3 m
78.4 m
80.5 m
79.2 m
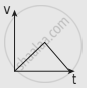
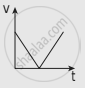
A ball is projected vertically upwards with a velocity v. It comes back to the ground in time t. Which v-t graph shows the motion correctly?
If one object is dropped vertically downward and another object is thrown horizontally from the same height, then the ratio of vertical distance covered by both objects at any instant t is ______
1
2
4
0.5
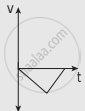
A ball is dropped from some height towards the ground. Which one of the following represents the correct motion of the ball?
If a particle executes uniform circular motion in the xy plane in a clockwise direction, then the angular velocity is in ______
+y direction
+z direction
-z direction
-x direction
If a particle executes uniform circular motion, choose the correct statement.
The velocity and speed are constant.
The acceleration and speed are constant.
The velocity and acceleration are constant.
The speed and magnitude of acceleration are constant.
If an object is thrown vertically up with the initial speed u from the ground, then the time taken by the object to return back to the ground is ______
`u^2/(2g)`
`u^2/(g)`
`u/(2g)`
`(2u)/g`
Two objects are projected at angles 30° and 60° respectively with respect to the horizontal direction. The range of two objects is denoted as R30° and R60°. Choose the correct relation from the following.
R30° = R60°
R30° = 4R60°
R30° = `R_{60°}/2`
R30° = 2R60°
An object is dropped in an unknown planet from a height of 50 m, it reaches the ground in 2 s. The acceleration due to gravity in this unknown planet is ______
g = 20 m s-2
g = 25 m s-2
g = 15 m s-2
g = 30 m s-2
Short Answer Questions
Explain what is meant by Cartesian coordinate system?
Define a vector. Give examples?
Define a scalar. Give examples?
Write a short note on the scalar product between two vectors.
Write a short note on the vector product between two vectors.
How do you deduce that two vectors are perpendicular?
Define displacement.
Define distance.
Define velocity.
Define speed.
Define acceleration.
What is the difference between velocity and average velocity?
Define a radian?
Define angular displacement.
Define angular velocity.
What is non-uniform circular motion?
Write down the kinematic equations for angular motion.
Write down the expression for angle made by resultant acceleration and radius vector in the non-uniform circular motion.
Long Answer Questions
Explain in detail the triangle law of addition.
Discuss the properties of scalar and vector products.
Derive the kinematic equations of motion for constant acceleration.
Derive the equations of motion for a particle (a) falling vertically (b) projected vertically.
Derive the equation of motion, range, and maximum height reached by the particle thrown at an oblique angle θ with respect to the horizontal direction.
Derive the expression for centripetal acceleration.
Derive the expression for total acceleration in the non-uniform circular motion.
The position vector particle has a length of 1m and makes 30° with the x-axis. What are the lengths of the x and y components of the position vector?
A particle has its position moved from `vecr_1 = 3hati + 4hatj` to `vecr_2 = hati + 2hatj`. Calculate the displacement vector `(∆vecr)` and draw the `vecr_1, vecr_2` and `Deltavecr` vector in a two dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.
Calculate the average velocity of the particle whose position vector changes from `vecr_1 = 5hati + 6hatj` to `vecr_2 = 2hati + 3hatj` in a time 5 second.
Convert the vector `vecr = 3hati + 2hatj` into a unit vector.
What are the resultants of the vector product of two given vectors given by `vecA = 4hati - 2hatj + hatk` and `vecB = 5hati + 3hatj - 4hatk`?
An object at an angle such that the horizontal range is 4 times the maximum height. What is the angle of projection of the object?
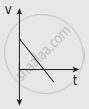
The following graphs represent the velocity-time graph. Identify what kind of motion a particle undergoes in each graph.
| (a) | 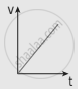 |
| (b) | 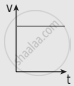 |
| (c) | 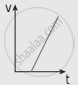 |
| (d) |  |
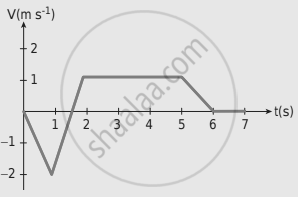
The following velocity-time graph represents a particle moving in the positive x-direction. Analyze its motion from 0 to 7 s. Calculate the displacement covered and distance travelled by the particle from 0 to 2 s.
A particle is projected at an angle of θ with respect to the horizontal direction. Match the following for the above motion.
(a) vx – decreases and increases
(b) vy – remains constant
(c) Acceleration – varies
(d) Position vector – remains downward
A water fountain on the ground sprinkles water all around it. If the speed of the water coming out of the fountain is v. Calculate the total area around the fountain that gets wet.
The following table gives the range of a particle when thrown on different planets. All the particles are thrown at the same angle with the horizontal and with the same initial speed. Arrange the planets in ascending order according to their acceleration due to gravity, (g value).
| Planet | Range |
| Jupiter | 50 m |
| Earth | 75 m |
| Mars | 90 m |
| Mercury | 95m |
The resultant of two vectors A and B is perpendicular to vector A and its magnitude is equal to half of the magnitude of vector B. Then the angle between A and B is
30°
45°
150°
120°
Compare the components for the following vector equations
(a) `"T"hatj - "mg"hatj = "ma"hatj`
(b) `vecT + vecF = vecA + vecB`
(c) `vecT - vecF = vecA - vecB`
(d) `"T"hatj + "mg"hatj = "ma"hatj`
Calculate the area of the triangle for which two of its sides are given by the vectors `vecA = 5hati - 3hatj, vecB = 4hati + 6hatj`
If Earth completes one revolution in 24 hours, what is the angular displacement made by Earth in one hour? Express your answer in both radian and degree.
An object is thrown with an initial speed of 5 m s-1 with an angle of projection of 30°. What is the height and range reached by the particle?
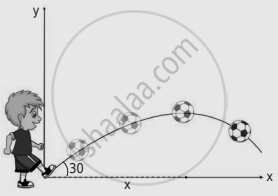
A football player hits the ball with a speed of 20 m s-1 with an angle of 30° with respect to horizontal direction as shown in the figure. The goal post is at a distance of 40 m from him. Find out whether the ball reaches the goal post?
If an object is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of 10 ms -1 from the top of a building of height 100 m. What is the horizontal distance covered by the particle?
An object is executing uniform circular motion with an angular speed of `pi/12` radians per second. At t = 0 the object starts at an angle θ = 0 What is the angular displacement of the particle after 4 s?
Consider the x-axis as representing east, the y–axis as north, and the z-axis as vertically upwards. Give the vector representing each of the following points.
a) 5 m northeast and 2 m up
b) 4 m southeast and 3 m up
c) 2 m northwest and 4 m up
The Moon is orbiting the Earth approximately once in 27 days, what is the angle transversed by the Moon per day?
An object of mass m has angular acceleration α = 0.2 rad s-2. What is the angular displacement covered by the object after 3 seconds? (Assume that the object started with angle zero with zero angular velocity).
Solutions for 2: Kinematics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 2 - Kinematics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 2 - Kinematics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 2 - Kinematics
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 2 (Kinematics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 2 Kinematics are Introduction to Kinematics, Concept of Rest and Motion, Elementary Concept of Vector Algebra, Multiplication of Vector by a Scalar, Position Vectors, Distance and Displacement, Differential Calculus, Integral Calculus, Motion Along One Dimension, Projectile Motion, Components of Vector.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Kinematics exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Kinematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.