Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain various types of friction.
Solution
There are two types of Friction:
(1) Static Friction:
Static friction is the force that opposes the initiation of motion of an object on the surface. The magnitude of static frictional force fs lies between
0 ≤ fs ≤ μsN
where, µs – coefficient of static friction
N – Normal force
(2) Kinetic friction:
The frictional force exerted by the surface when an object slides is called kinetic friction. Also called sliding friction or dynamic friction,
fk – µkN
where µk – the coefficient of kinetic friction
N – Normal force exerted by the surface on the object
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the empirical laws of static and kinetic friction.
A heavy uniform chain lies on a horizontal table. If the coefficient of friction between the chain and the table is 0.25, then the maximum fraction of the length of the chain that can hang over one edge of the table is
A block of mass 20 kg is sliding on a surface is inclined at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. What will be the acceleration of the block if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.7?
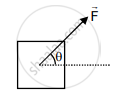
A block of mass m slides along a floor while a force of magnitude F is applied to it at an angle θ as shown in figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction is µK. Then, the block's acceleration 'a' is given by ______.
(g is acceleration due to gravity)
A uniform chain of length 3 metres and mass 3 kg overhangs a smooth table with 2 metres laying on the table. If k is the kinetic energy of the chain in joule as it completely slips off the table, then the value of k is ______.
(Take g = 10 m/s2)
A block of mass m is pulled by a constant power P placed on a rough horizontal plane. The friction co-efficient between the block and the surface is µ. Maximum velocity of the block will be:
A block of mass m = 1 kg moving on horizontal surface with speed u = 2 m/s enters a rough horizontal patch ranging from x = 0.10 m to x = 2.00 m. If the retarding force fr on the block in this range is inversely proportional to x over this range i.e.
fr = `"-k"/x` 0.10 < x < 2.00
= 0 for x < 0.10 and x > 2.00
If k = 0.5 J then the speed of this block as it crosses the patch is (use ℓn 20 = 3)
Block A has a mass of 2 kg and block B has 20 kg. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the horizontal surface is 0.1, and B is accelerating towards the right with a = 2 m/s2, then the mass of the block C will be ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)

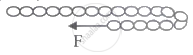
A chain of mass 'M' and length 'L' is put on a rough horizontal surface and is pulled by constant horizontal force 'F' as shown in the figure. The velocity of the chain as it turns completely ______.
(Coefficient of friction = μ)
A body starts from rest on a long inclined plane of slope 45°. The coefficient of friction between the body and the plane varies as µ = 0.3 x, where x is distance travelled down the plane. The body will have maximum speed (for g = 10 m/s2) when x = ______.
