Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain various types of friction.
उत्तर
There are two types of Friction:
(1) Static Friction:
Static friction is the force that opposes the initiation of motion of an object on the surface. The magnitude of static frictional force fs lies between
0 ≤ fs ≤ μsN
where, µs – coefficient of static friction
N – Normal force
(2) Kinetic friction:
The frictional force exerted by the surface when an object slides is called kinetic friction. Also called sliding friction or dynamic friction,
fk – µkN
where µk – the coefficient of kinetic friction
N – Normal force exerted by the surface on the object
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of mass m begins to move on the plane inclined at an angle θ. The coefficient of static friction of inclined surfaces is µs. The maximum static friction experienced by the mass is ______
Suggest a few methods to reduce friction.
State the empirical laws of static and kinetic friction.
People often say “For every action, there is an equivalent opposite reaction”. Here they meant ‘action of a human’. Is it correct to apply Newton’s third law to human actions? What is mean by ‘action’ in Newton's third law? Give your arguments based on Newton’s laws.
Briefly explain ‘rolling friction.'
A uniform metal chain is placed on a rough table such that one end of the chain hangs down over the edge of the table. When two-thirds of its chain length hangs over the edge the chain start sliding. Then the coefficient of static friction is:
The minimum radius of a circle along which a cyclist can ride with a velocity 18 km/hr if the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road is µ = 0.5, is ______ (Take g = 10 m/s2)
Block A has a mass of 2 kg and block B has 20 kg. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the horizontal surface is 0.1, and B is accelerating towards the right with a = 2 m/s2, then the mass of the block C will be ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)

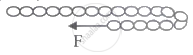
A chain of mass 'M' and length 'L' is put on a rough horizontal surface and is pulled by constant horizontal force 'F' as shown in the figure. The velocity of the chain as it turns completely ______.
(Coefficient of friction = μ)
A block of mass 10 kg starts sliding on a surface with an initial velocity of 9.8 ms-1. The coefficient of friction between the surface and bock is 0.5. The distance covered by the block before coming to rest is ______.
[use g = 9.8 ms-2]
